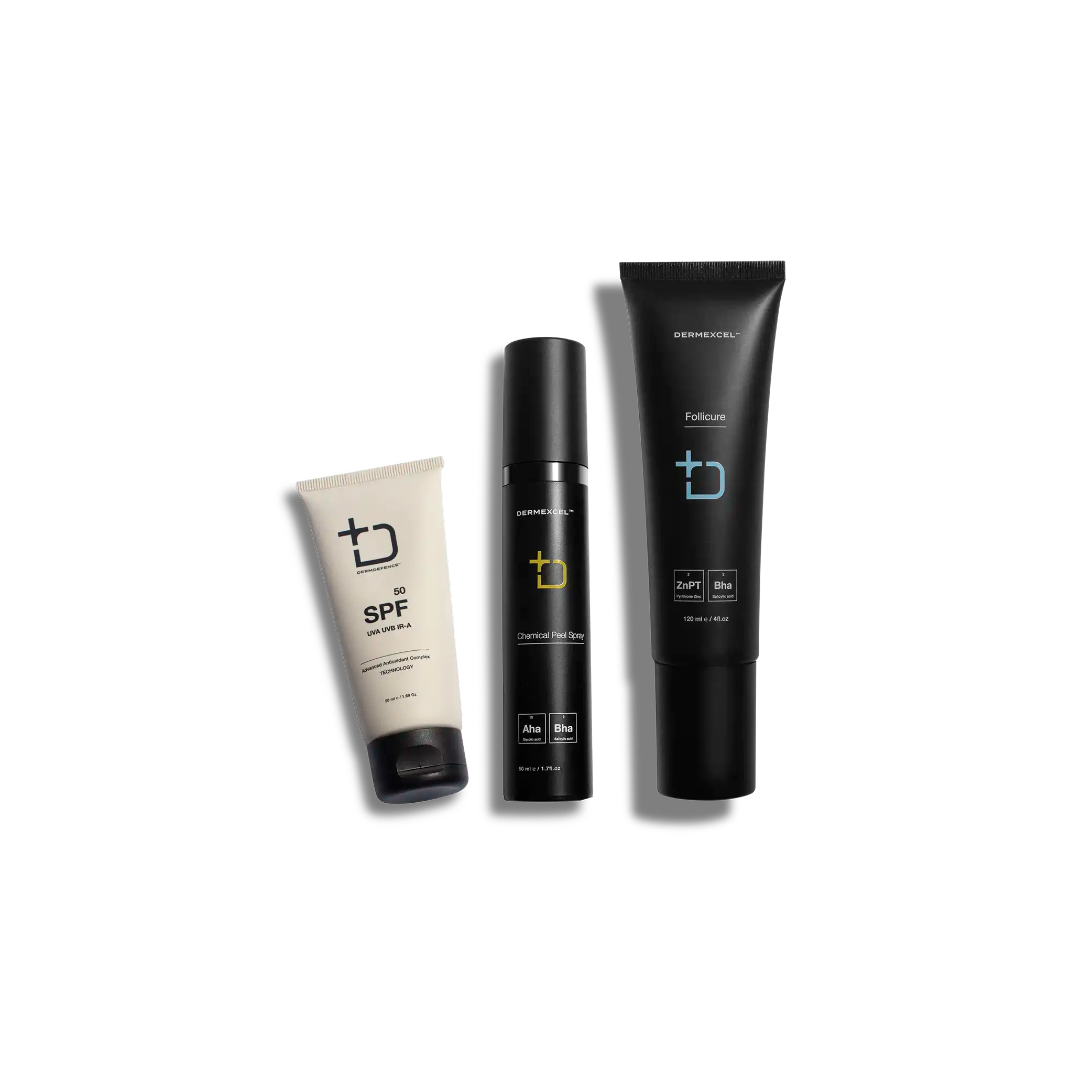
Treatment Pack for Mild Body Breakouts
Free Gifts with your treatment pack

Mini Silicone Scalp Massager

Cotton Bag




Choose options
Body Breakouts Treatment
Treatment Objectives
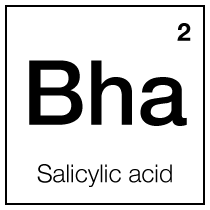
Regulate sebum (oil) production
Inflammation Control
Treat Acne Effectively
Improve Skin Texture
Unclog pores
Support Healthy Skin Renewal
Subheading
Heading
Body Breakouts Treatment
products in your treatment pack
Testimonials