your dermal diagnosis™ results
Good day,
We're thrilled you're taking proactive steps to understand your skin better.
Below, you'll find your most recent Dermal Diagnosis™ results. Use this data as a roadmap to achieving healthier skin.
| Date | Dermal Diagnosis™ | Profile and Treatment Plan |
|---|---|---|
DERMAL DIAGNOSIS™ RESULT BREAKDOWN
| Aging Score | Hydration Score | Pigmentation Score | Inflammation category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Dermal Diagnosis™ |
|---|---|
DERMAL DIAGNOSIS™ RESULT BREAKDOWN
| Aging Score | |
| Hydration Score | |
| Pigmentation Score | |
| Inflammation category |
's Dermal Diagnosis™ Profile:
Acne Breakouts: Grade 1
your frustrations
- Sensitive skin that may react to various stimuli and products.
- Impaired skin barrier and altered skin microbiome.
- Rough skin texture with inflammation and breakouts.
- Congested pores in the form of blackheads and whiteheads.
your goals
- No stinging; itching; burning; or other skin discomforts.
- Protected and healed skin barrier with balanced microbiome.
- Smooth skin texture with no breakouts and inflammation.
- Clean pores.

minimal impact

easier management

fast treatment response

early intervention
-
Low Risk of Scarring: Since this level of acne involves fewer and less severe lesions, there is a lower risk of skin scarring compared to more severe grades of acne.
-
Minimal Impact on Appearance: The visibility of acne is less pronounced in grade 1, which might have less impact on self-esteem and social interactions than more severe cases.
-
Faster Response to Treatment: Mild acne often responds quickly to treatment, allowing for a shorter duration of therapy and quicker improvement in skin appearance.
-
Preventive Opportunity: Effective management of grade 1 acne can prevent its progression to more severe forms, helping to maintain skin health over time.
-
Easier Management: Grade 1 acne is typically easier to manage, and more invasive procedures are unnecessary. These products can have more significant side effects and require closer medical supervision.

Congested Pores

Acne Breakouts

Sebum Control
-
Mild Breakouts: Even occasional or mild breakouts require attention, as they can lead to inflammation, discomfort, and potential scarring or pigmentation changes.
-
Skin Discoloration: Mild acne can still cause hyperpigmentation or post-inflammatory erythema (red marks), especially in individuals with lighter or darker skin tones who may be more prone to color changes in the skin.
-
Sebum Control: Controlling excess oil and shine, especially in the T-zone area, can be a constant struggle, affecting the skin's overall appearance.
-
Psychological Impact: Acne of any grade can affect self-esteem and mental health. The visibility of even mild acne can lead to self-consciousness or social anxiety, particularly in teenagers and young adults.
-
Inflammation: Even mild acne involves some level of inflammation which can lead to discomfort and redness. Chronic inflammation can also disrupt the skin barrier and increase sensitivity.
-
Risk of Aggravation: Certain lifestyle factors like diet, stress, and incorrect skincare can aggravate even mild acne, leading to flare-ups or progression to more severe forms.
Acne Breakouts: Grade 1
Treatment objectives

Regulate sebum (oil) production
Teenage years often see an increase in oil production due to hormonal changes. Treatment should aim to regulate this sebum production, preventing the skin from becoming excessively oily.

Unclog pores
Dissolve and extract cellular debris and prevent skin cells from clumping together in pores to ensure that the pores remain clear and free from blockages, which can lead to breakouts.

Reduce Inflammation
Down-regulate the inflammatory response, balance the skin microbiome and prevent bacterial infiltration.

Reduce and eliminate acne breakouts
Prevent and manage all the factors leading to comedones and acne lesions.

DNA Protection and Repair
Safeguard and repair UV-induced DNA damage, utilizing a blend of UV defense, Retinol, Niacinamide, and antioxidants. This strategy prevents future damage and aids in the repair of existing cellular impairments.

Support Healthy Skin Renewal
Adolescence is a time of rapid skin cell turnover. This treatment aims to support this process, promoting a fresh, youthful appearance.
Acne Breakouts: Grade 1
Beneficial Active Ingredients
Zinc Pyrithione
Zinc pyrithione, a compound with potent antifungal and antibacterial properties, has established itself as a cornerstone in the treatment of various skin conditions, particularly those involving Malassezia yeast. Its effectiveness against seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff, which are often associated with an overgrowth of Malassezia species, makes it a key ingredient for many dermatological conditions.
Zinc pyrithione’s mode of action is multifaceted, primarily targeting the membrane of fungi and bacteria, thereby disrupting their growth and replication. One of its significant mechanisms involves inhibiting fungal cell membrane transport by blocking the energy production pathway, which is crucial for cell survival.
In Malassezia, yeast, a natural inhabitant of the skin flora, can overgrow and cause conditions like seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff; zinc pyrithione's antifungal action is particularly beneficial. It reduces the yeast population on the skin, thereby alleviating the symptoms associated with its overgrowth, such as flaking, irritation, and redness.
Its efficacy in treating seborrheic dermatitis is attributed to its ability to reduce the Malassezia count, diminish inflammatory responses, and soothe the skin. Similarly, in dandruff, which is often linked to an excess of Malassezia, zinc pyrithione effectively reduces flaking and itchiness, promoting a healthier scalp environment.
The efficacy of zinc pyrithione in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff is well-documented. Its safety profile and efficacy have been confirmed by numerous studies, with significant improvements observed in both scalp and skin conditions following regular use.
Physiological Effects
- Antifungal Activity: It is effective against a range of fungi, including those that cause dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. Zinc Pyrithione inhibits the division of fungal cells, reducing their proliferation.
- Antibacterial Properties: This compound also exhibits antibacterial activity, making it useful in treating and preventing bacterial skin infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Zinc Pyrithione can reduce inflammation, which is beneficial in alleviating symptoms of various inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps in regulating sebum production, which can be beneficial for oily skin and conditions like acne.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis: Zinc Pyrithione is a common ingredient in anti-dandruff shampoos and is effective in controlling the flaking and itching associated with these conditions.
- Psoriasis: It can help manage the symptoms of psoriasis, particularly in reducing scaling and redness.
- Acne: Due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, Zinc Pyrithione can be beneficial in the treatment of acne.
- Fungal Infections: It is effective in treating various fungal skin infections due to its antifungal properties.
References
- Warshaw, E. M., et al. (2005). Efficacy of Zinc Pyrithione in Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff. Dermatology.
- Pierard-Franchimont, C., et al. (2002). Antidandruff shampoo efficacy in dandruff/seborrhoeic dermatitis. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Scheman, A., et al. (2000). Antimicrobial Activity of Zinc Pyrithione. American Journal of Infection Control.
Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is highly acclaimed for its remarkable exfoliating and rejuvenating properties. Its small molecular size enables deep skin penetration, fostering efficient exfoliation at the cellular level.
Glycolic acid’s water solubility allows it to penetrate the upper layers of the skin easily. Its primary mechanism of action involves weakening the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their shedding, and revealing the newer, healthier skin beneath. This process of accelerated cell turnover is instrumental in addressing a range of skin concerns, from aging signs like fine lines and wrinkles to texture irregularities and hyperpigmentation.
Glycolic acid's efficacy extends beyond mere exfoliation. It's also recognized for stimulating collagen production, a crucial protein in maintaining skin's elasticity and firmness. This aspect contributes to its anti-aging benefits. Furthermore, its hydrating properties add to its appeal, as they help increase the skin's capacity to retain moisture, leading to a more supple and vibrant complexion.
Clinical studies have consistently supported glycolic acid's role in improving skin appearance. Research indicates significant improvements in skin texture and pigmentation and the visible reduction of wrinkles and fine lines with glycolic acid.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: Glycolic acid is a powerful exfoliant. It dissolves the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, facilitating their removal and revealing newer, healthier skin underneath.
- Increased Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for skin elasticity and firmness. This action helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Enhanced Skin Hydration: Glycolic acid improves the skin's ability to retain moisture, enhancing hydration and a more plump, vibrant skin appearance.
- Skin Brightening: Removing dead skin cells can brighten the complexion and reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Improved Skin Texture: Regular use of glycolic acid can lead to smoother, more even textured skin, making it beneficial for conditions like keratosis pilaris.
- Acne Treatment: Its exfoliating properties help in unclogging pores, thereby reducing the occurrence of acne breakouts.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Glycolic acid is widely used in anti-aging products to reduce signs of aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: It helps manage acne by exfoliating the skin and removing blockage from pores.
- Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats hyperpigmentation by accelerating the removal of hyperpigmented skin cells.
- Textural Irregularities: Glycolic acid can improve skin texture and is beneficial for treating keratosis pilaris and other conditions of rough skin.
- Sun-Damaged Skin: It helps rejuvenate sun-damaged skin by accelerating cell turnover and collagen synthesis.
References
- Bernstein, E. F. (2001). Glycolic acid treatment increases type I collagen mRNA and hyaluronic acid content of human skin. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Sharad, J. (2013). Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 35(3), 388-391.
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid, a renowned beta hydroxy acid (BHA), is a cornerstone in dermatology and skincare due to its exceptional keratolytic and comedolytic properties. Its unique ability to penetrate oil-laden hair follicle pores makes it particularly effective in treating acne-prone and oily skin types.
Salicylic acid dissolves skin debris (sebum and dead skin cells) that clogs pores and causes acne. It's a mild antibacterial and powerful anti-inflammatory agent that helps reduce the redness and swelling associated with breakouts.
What sets salicylic acid apart in dermatological treatments is its ability to exfoliate the skin, not just on the surface but within the pores themselves. This is due to its oil-soluble nature, which allows it to penetrate deep into the pores and dissolve the keratin plugs that lead to blackheads and whiteheads.
Furthermore, salicylic acid also has the capacity to adjust the pH of the skin, creating an environment less favorable for the growth of acne-causing bacteria. Salicylic acid's efficacy in treating various skin conditions, particularly acne, has been extensively documented in the scientific literature. Studies have consistently shown its ability to reduce acne lesions in terms of count and severity. Additionally, salicylic acid is highly recommended for its effectiveness in treating other skin conditions, such as psoriasis and dandruff, due to its ability to soften and remove scales and flakes from the skin.
Physiological Effects
- Keratolytic Action: Salicylic acid is known for its ability to exfoliate the skin by dissolving the intercellular 'glue' that holds skin cells together, helping to remove dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- Comedolytic Effect: It is particularly effective in reducing comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) by unclogging pores and preventing the formation of new comedones.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Salicylic acid reduces inflammation, which is beneficial in treating acne and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps to regulate oil production, making it a valuable ingredient for managing oily and acne-prone skin.
- Penetration Enhancement: Due to its lipophilic nature, it can penetrate sebum-filled follicles, effectively treating acne located deep within the pores.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne Vulgaris: Salicylic acid is a cornerstone in acne treatment, effectively preventing and treating existing acne lesions.
- Psoriasis: Its keratolytic properties make it helpful in softening and removing scales associated with psoriasis.
- Warts: Salicylic acid is commonly used to treat warts because it can exfoliate and remove thick skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: It helps manage seborrheic dermatitis by reducing scaling and redness.
- Keratosis Pilaris: Salicylic acid can aid in smoothing the rough bumps associated with peratosis Pilaris.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 3, 135.
- Zander, E., & Weisman, S. (1992). Treatment of acne vulgaris with salicylic acid pads. Clinical Therapeutics.
- Gupta, A. K., & Nicol, K. (2004). The use of sulfur in dermatology. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
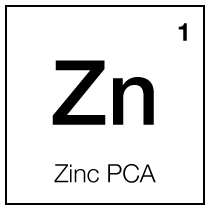
Zinc PCA
Zinc PCA, also known as Zinc Pyrrolidone Carboxylic Acid, is a skin care ingredient that combines the mineral zinc with a hydrating molecule PCA (Pyrrolidone Carboxylic Acid). It is renowned for its numerous benefits in skincare, particularly for its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and sebum-regulating properties.
Zinc PCA is derived from zinc, an essential mineral known for its antioxidant and skin-soothing capabilities. Zinc is also noted for its role in wound healing and its ability to reduce inflammation, which can be particularly beneficial for acne-prone and irritated skin. The PCA component is a natural moisturizing factor (NMF) found in the skin, which helps maintain the skin's hydration levels.
One of the key benefits of Zinc PCA is its ability to regulate sebum production. Excess sebum can lead to acne and oily skin, and Zinc PCA helps to moderate this by inhibiting the activity of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which is involved in oil production. This makes it an effective ingredient in formulations targeting oily and acne-prone skin (Schueller, R. and Romanowski, P., 2003).
In addition to its sebum-regulating properties, Zinc PCA possesses antimicrobial properties, which further contribute to its efficacy in treating acne. By reducing the presence of acne-causing bacteria on the skin, it helps to prevent and reduce acne breakouts.
Moreover, Zinc PCA's anti-inflammatory properties make it beneficial for soothing irritated skin and reducing redness and inflammation associated with various skin conditions, including acne, rosacea, and eczema.
Physiological Effects
- Sebum Regulation: Zinc PCA reduce and regulate sebum secretion and production, making it beneficial for oily and acne-prone skin by controlling excess oil production.
- Antimicrobial Action: Zinc has antimicrobial properties, particularly effective against acne-causing bacteria, reducing acne breakouts.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Zinc PCA reduces inflammation, which is beneficial in treating inflammatory skin conditions like acne and rosacea.
- Moisture Retention: PCA is a natural moisturizing factor (NMF) that helps maintain skin hydration, enhancing the skin’s moisture retention capabilities.
- Wound Healing: Zinc is essential for wound healing processes, aiding in the repair and regeneration of skin tissues.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne Management: Its ability to regulate sebum production and provide antimicrobial action makes Zinc PCA a valuable ingredient in acne treatments.
- Oily Skin: It's beneficial in controlling excess oiliness and maintaining a balanced skin environment.
- Sensitive Skin Conditions: Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, Zinc PCA soothes sensitive skin and conditions like rosacea.
- Skin Hydration: Its role as an NMF helps in maintaining skin hydration, useful in treating dry skin conditions.
References
- Schagen, S. K., et al. (2012). Discovering the link between nutrition and skin aging. Dermato-endocrinology.
- Firooz, A., et al. (2011). Zinc therapy in dermatology: a review. Dermatology Research and Practice.
- Gupta, M., et al. (2014). Zinc therapy in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal.
- Schueller, R. and Romanowski, P. (2003). Conditioning Agents for Hair and Skin. Cosmetic Science and Technology Series. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, USA.
Infraguard™
Infraguard™ is a novel and powerful antioxidant powerhouse designed to protect the skin from the potentially harmful effects of electromagnetic radiation, specifically from 5G networks, blue light, and other environmental stressors. It shields the skin against oxidative stress and inflammation, prevents premature aging, and maintains overall health.
Infraguard® is a multifunctional ingredient that extends beyond traditional sun protection. It addresses the broader spectrum of light-induced skin damage and oxidative stress, provides DNA protection, and offers anti-aging benefits. Its inclusion in the DermExcel sunscreens represents an advanced step in comprehensive skin care, targeting UV rays and the often-overlooked infrared and blue light, ensuring a more holistic approach to maintaining skin health and appearance.
Physiological Effects
- Protection Against Blue Light and Infrared (IR) Radiation: Infraguard is formulated to shield the skin from the harmful effects of blue light and IR radiation, which can lead to premature skin aging and damage.
- Antioxidant Properties: It has strong antioxidant capabilities, helping to neutralize free radicals induced by environmental stressors such as pollution, IR, and blue light.
- Anti-Aging Benefits: By protecting against IR radiation and mitigating oxidative stress, Infraguard helps to prevent signs of aging like wrinkles and loss of skin elasticity.
- Skin Barrier Protection: Infraguard strengthens the skin's natural barrier, enhancing its resilience against environmental factors.
- DNA Protection: Infraguard™ aids in shielding the DNA in skin cells from damage caused by environmental aggressors. This is crucial in maintaining the integrity of skin cells and preventing mutations that can lead to skin aging and other skin-related issues.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Preventing Photoaging: Infraguard's ability to protect against IR and blue light makes it beneficial in preventing photoaging, a key concern in modern dermatology. Infrared light can penetrate deeper into the skin than UV rays, potentially leading to increased collagen degradation and skin laxity. Infraguard® helps mitigate these effects.
- Combatting Environmental Stressors: Its antioxidant properties protect the skin from various environmental pollutants and stressors.
- Supporting Skin Health: Infraguard contributes to overall skin health by improving the skin's barrier function and providing antioxidant support.
- Suitability for Diverse Skin Conditions: Given its protective and anti-aging properties, Infraguard is suitable for use in various dermatological conditions, especially environmental damage and aging.
References
- Kappler, Katharina et al. "Development of an in Vitro Assay to Evaluate the Biological Impact of 5G Technology on Human Skin. Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications, 2022, vol. 12, pp. 100-108. DOI: 10.4236/jcdsa.2022.122009.
- Extensive references cited within the research article including studies on 5G technology, health effects, and skin biology.
Vitamin E
The fat-soluble Vitamin E's benefits in maintaining skin health and appearance are well-acknowledged in both cosmetic and clinical dermatology. Comprising a group of eight compounds, including four tocopherols and four tocotrienols, Vitamin E is known for its role in protecting cell membranes from oxidative damage.
Vitamin E is celebrated in skincare for its ability to neutralize free radicals caused by environmental stressors such as UV radiation and pollution. These free radicals can lead to premature skin aging, making Vitamin E a valuable ingredient in anti-aging skincare products. Its antioxidant action helps to protect the skin from damage, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and improve skin texture and tone.
Additionally, Vitamin E is known for its moisturizing benefits. It helps to strengthen the skin barrier, reduce moisture loss, and keep the skin hydrated and supple. This makes it especially beneficial for dry and damaged skin.
Vitamin E also has anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial in soothing and calming irritated skin. This has implications for conditions such as dermatitis and acne, where inflammation plays a key role.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Protection: Vitamin E neutralizes harmful free radicals in the skin, preventing oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
- Moisturization: It has moisturizing properties, helping to improve skin hydration and alleviate dryness.
- Wound Healing: Vitamin E may assist in the skin's healing process, although its efficacy in wound healing is still a subject of research.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it can provide some degree of photoprotection by strengthening the skin's defense against UV-induced damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: It helps reduce skin inflammation and is beneficial in managing conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Its antioxidant properties make it useful in anti-aging skincare products to protect against free radical damage and improve skin appearance.
- Dry Skin Conditions: Vitamin E's moisturizing effects are beneficial in treating dry skin and improving overall skin texture.
- Inflammatory Skin Diseases: It can be helpful in soothing inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
- Sun Protection and Repair: Vitamin E is included in sunscreens and after-sun products for its ability to mitigate sun damage.
- Scar Treatment: Some studies suggest Vitamin E may help reduce the appearance of scars, although evidence is mixed.
References
- Thiele, J. J., Hsieh, S. N., & Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S. (1998). Vitamin E: Critical Review of Its Current Use in Cosmetic and Clinical Dermatology. Dermatologic Surgery, 24(7), 805–813.
- Ratz-Łyko, A., & Arct, J. (2016). Anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties of active skin care ingredients. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 9(9), 36–40.
- Keen, M. A., & Hassan, I. (2016). Vitamin E in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal.
- Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S., & Thiele, J. (2007). Vitamin E in human skin: Organ-specific physiology and considerations for its use in dermatology. Molecular Aspects of Medicine.
- Nachbar, F., & Korting, H. C. (1995). The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin. Journal of Molecular Medicine.
Sunscreen
Using sunscreen is a fundamental aspect of skin care and preventive dermatology. It's essential for reducing the risk of skin cancers and photoaging and maintaining overall skin health in the face of constant exposure to UV radiation.
Sunscreen is a vital skincare product designed to protect the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Two primary types of UV radiation affect the skin: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and are primarily responsible for aging and long-term skin damage, whereas UVB rays cause sunburn and play a key role in developing skin cancer.
Sunscreen products work by either absorbing, reflecting, or scattering sunlight. They contain chemical compounds that absorb UV radiation and convert it into a small amount of heat or physical compounds (like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) that act as a physical barrier, reflecting UV light away from the skin.
The effectiveness of sunscreen is measured by its Sun Protection Factor (SPF). SPF indicates how well the sunscreen protects against UVB rays. For example, an SPF of 30 means it would take 30 times longer for your skin to burn than without sunscreen. However, it's important to note that no sunscreen can block 100% UV rays.
Regular use of sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 can reduce the risk of skin cancer, prevent sunburn, and slow down the skin's aging process.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Prevention of Sunburn: Sunscreen protects the skin from UVB rays, which cause sunburn. This reduces the immediate risk of skin damage and discomfort.
- Skin Cancer Prevention: Regular use of sunscreen significantly lowers the risk of developing various types of skin cancer, especially melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma.
- Prevention of Photoaging: Sunscreen also shields the skin from UVA rays, which penetrate deeper into the skin and are primarily responsible for photoaging, including wrinkles, leathery skin, and sunspots.
- Protection Against Photosensitivity: Sunscreen helps prevent flare-ups triggered by sun exposure for individuals with photosensitive skin conditions like lupus or rosacea.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: It aids in preventing and managing hyperpigmentation and melasma, conditions exacerbated by sun exposure.
- General Skin Health: Sunscreen helps maintain overall skin health and integrity by protecting the skin from UV damage.
References
- Burnett, M. E., & Wang, S. Q. (2011). Current sunscreen controversies: a critical review. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine.
- Green, A. C., et al. (2011). Reduced melanoma after regular sunscreen use: randomized trial follow-up. Journal of Clinical Oncology.
- Hughes, M. C. B., et al. (2013). Sunscreen and Prevention of Skin Aging: A Randomized Trial. Annals of Internal Medicine.
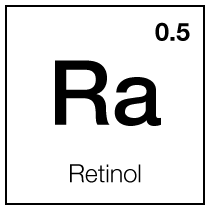
Retinoic acid analogue
Retinoic acid, often referred to as tretinoin in its pharmaceutical form, is the active form of Vitamin A. It is widely recognized for its powerful effects in dermatology and skin care, particularly in treating acne and signs of skin aging.
Retinoic acid works at the cellular level to modify gene expression and affect cell growth. In treating acne, it promotes the turnover of skin cells, reducing the likelihood of pore-clogging and helping to clear existing breakouts. Additionally, it decreases the cohesiveness of follicular epithelial cells, further preventing the formation of comedones.
Retinoic acid's ability to stimulate collagen production is a key benefit in anti-aging skincare. This leads to a reduction in fine lines and wrinkles and an improvement in overall skin texture and tone. It also aids in skin discoloration and hyperpigmentation by accelerating cell turnover, bringing new skin cells to the surface faster, and shedding pigmented and damaged cells.
Despite its benefits, retinoic acid can irritate the skin, causing side effects like redness, dryness, and peeling, especially during the initial period of use. Its potency means it is generally available by prescription and requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional.
Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR), is a newer, esterified form of retinoic acid. Unlike cosmetic retinol, HPR binds directly to the retinoid receptors of the skin cells without the need for conversion. This direct binding allows it to deliver similar benefits to retinoic acid, such as stimulating collagen production, improving skin elasticity, and reducing signs of aging, but with a lower risk of irritation.
HPR is considered more gentle and less irritating than traditional retinoic acid while offering comparable benefits. With HPR, everyone has access to the benefits of prescription retinoids without the risk of side effects.
Physiological Effects
- Cell Turnover and Renewal: Promotes rapid cell turnover, aiding in the exfoliation of dead skin cells and the generation of new cells.
- Skin Texture: By promoting cell renewal it improves skin texture, addressing issues like roughness and dullness.
- Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, essential for reducing the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and improving skin elasticity.
- Acne Treatment: Effective in treating acne by unclogging pores and reducing the size of sebaceous glands, it diminishes both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions.
- Pigmentation: It can reduce hyperpigmentation by accelerating the turnover of hyperpigmented skin cells and inhibiting melanin production.
- Photoaging: Effective in treating signs of photoaging, reversing some of the damage caused by UV radiation.
Special Benefits
- Retinoid Receptor Activity: HPR, an ester of retinoic acid, binds directly to retinoid receptors in the skin, enabling it to work without needing to be converted into retinoic acid.
- Lower Irritation: It typically causes less irritation than retinoic acid, making it more suitable for sensitive skin types.
- Collagen Stimulation and Anti-Aging: Like retinoic acid, HPR helps in stimulating collagen production and has anti-aging properties.
- Acne and Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats acne and reduces hyperpigmentation, often with fewer side effects than retinoic acid.
- Stability and Penetration: HPR is more stable and lipid-soluble, so it penetrates the skin more effectively and is less prone to degradation.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., ... & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Fisher, G. J., Wang, Z. Q., Datta, S. C., Varani, J., Kang, S., & Voorhees, J. J. (1996). Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light. New England Journal of Medicine, 337(20), 1419-1428.
- Truchuelo, M. T., Jiménez, N., Jaén, P. (2018). Assessment of the efficacy of a new complex-based retinoic acid and retinol in a 3-month study using objective methods and skin biomarker analysis. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 17(3), 347-354.
- Mukherjee, S., et al. (2006). Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety. Clinical Interventions in Aging.
- Randhawa, M., et al. (2015). Hydroxypinacolone retinoate: a new retinoid and its use in dermatology. Skin Therapy Letter.
Broad Spectrum Filters
Tinosorb® M and Tinosorb® S represent sophisticated advancements in sun protection technology.
Tinosorb® M
- Biochemical Action: A unique UV filter due to its ability to function through absorption, reflection, and scattering of UV rays.
- Physiological Impact: The triple-action mechanism of Tinosorb® M offers comprehensive sun protection. By mitigating the penetration of both UVA and UVB rays, it significantly reduces the risk of DNA damage, photoaging, and carcinogenesis. Its ability to remain on the skin's surface reduces systemic exposure, making it a safer option with minimal potential for irritation or allergic reactions.
Tinosorb® S
- Biochemical Action: A broad-spectrum UV filter with a molecular structure that effectively absorbs both UVA and UVB rays. Additionally, it enhances the photostability of other UV filters, making the sunscreen formulation more effective over time.
- Physiological Impact: By providing extensive UVA and UVB protection, Tinosorb® S plays a crucial role in preventing short-term sun damage like sunburn and long-term risks such as skin aging and skin cancer. Its photostability ensures sustained protection during sun exposure, and its compatibility with other UV filters means it can be used to formulate sunscreens that are both effective and suitable for sensitive skin.
MORNING
EVENING
MORNING
EVENING
Morning Regimen Notes
For the best use of Medi-Zinc Cleanser, please check the detailed instructions on its product page. You can access this page by clicking the cleanser's name above.
Apply Inflacin Serum on dry skin every morning after cleansing.
Apply Dermdefence SPF 50 a few minutes after you apply your serum.
Evening Regimen Notes
For the best use of Medi-Zinc Cleanser, please check the detailed instructions on its product page. You can access this page by clicking the cleanser's name above.
- After cleansing, apply the Chemical Peel Spray to dry skin.
- Start using Chemical Peel Spray once a week, if your skin adjusts well, you can increase the frequency.
In the evenings, if you apply Chemical Peel Spray; don't layer it with another product. Other products can make Chemical Peel Spray less effective by changing its pH.
Important Notes
- Reduce the use of Chemical Peel Spray to one evening a week or even one evening every two weeks.
- When irritation subsides, slowly increase the frequency of use again, as tolerated by your skin.
(Based on your selection)
Your Grade 1 Acne Skin Type, characterized by an onset of mostly non-inflammatory blemishes, such as blackheads and whiteheads, highlights the initial challenges of managing and preventing acne without overwhelming your skin. While milder compared to more advanced forms of acne, this stage calls for proactive and mindful skincare to maintain clarity and prevent progression.
The primary feature of Grade 1 acne is the appearance of comedones, which are the result of pores clogged with excess sebum and dead skin cells. These blemishes, though not severely inflamed, can disrupt the smooth texture of your skin and, if not managed properly, can escalate into more problematic forms of acne.
A careful balance in your skincare regimen is crucial. Excess oil and environmental impurities need to be gently removed without stripping the skin’s natural moisture. This ensures that while your skin remains clean, it does not become overly dry or irritated, which can provoke further oil production.
Your journey with Grade 1 Acne Skin Type is about fostering balance and vigilance—managing oil production and keeping pores clear while nurturing the skin’s overall health. With consistent care and the appropriate products, your skin can maintain its clarity and smoothness, avoiding more severe acne developments. This proactive approach allows you to confidently manage your skin’s needs, reflecting your commitment to maintaining a healthy and vibrant complexion.
Acne Breakouts: Grade 1
your treatment pack
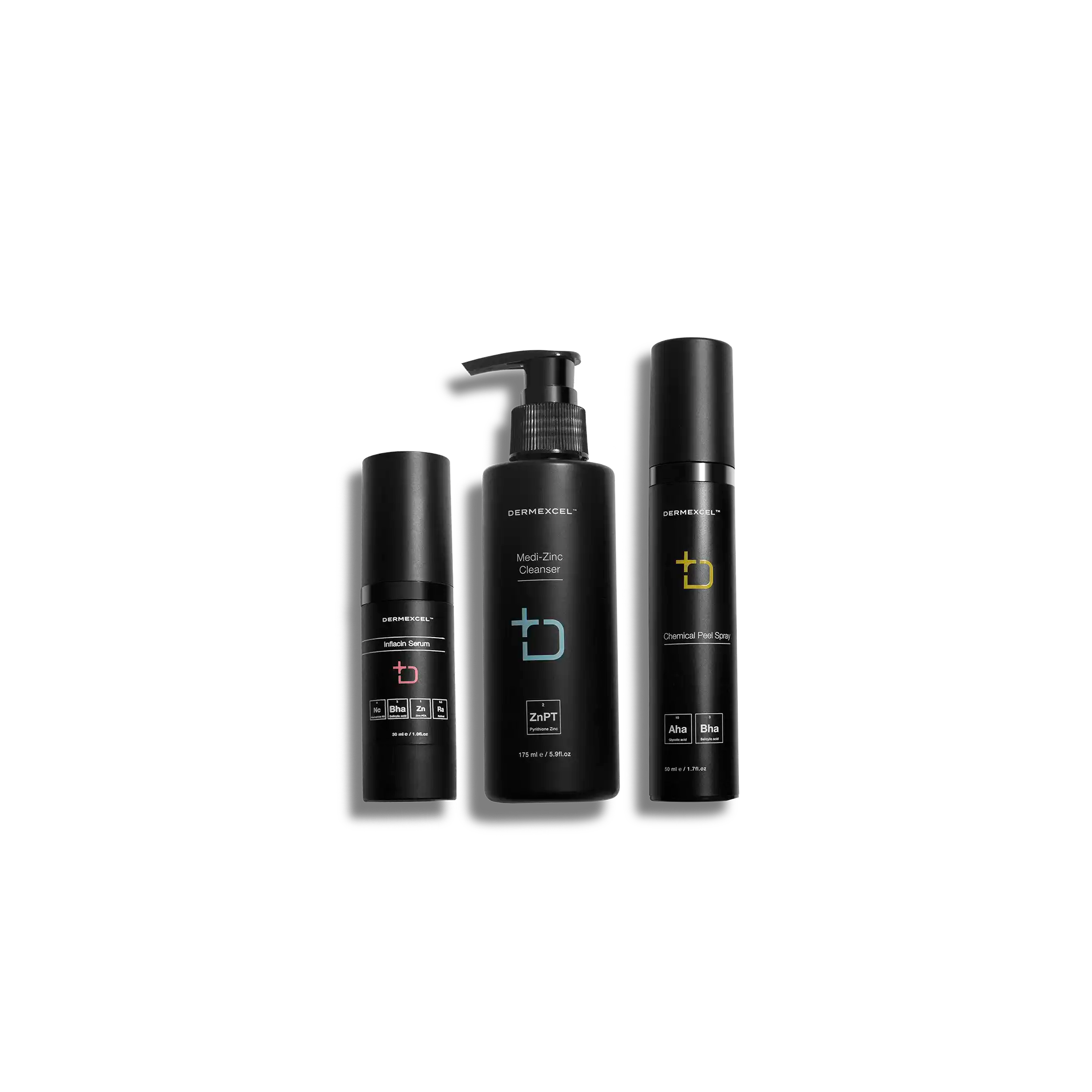






Treatment pack for Teenage Acne Grade 1

Anti-Acne

↓ inflammation

Unclog Pores

≈ microbiome

Regulate Sebum (oil)




Free Gifts with your treatment pack

Cotton Bag

Microfibre Sponge

Choose options


Treatment pack for Teenage Acne Grade 1
Acne Breakouts: Grade 1
products in your treatment pack








Itch Relief

Anti-Acne

↓ inflammation

anti-redness

Anti-microbial
Zinc Pyrithione
Zinc pyrithione, a compound with potent antifungal and antibacterial properties, has established itself as a cornerstone in the treatment of various skin conditions, particularly those involving Malassezia yeast. Its effectiveness against seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff, which are often associated with an overgrowth of Malassezia species, makes it a key ingredient for many dermatological conditions.
Zinc pyrithione’s mode of action is multifaceted, primarily targeting the membrane of fungi and bacteria, thereby disrupting their growth and replication. One of its significant mechanisms involves inhibiting fungal cell membrane transport by blocking the energy production pathway, which is crucial for cell survival.
In Malassezia, yeast, a natural inhabitant of the skin flora, can overgrow and cause conditions like seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff; zinc pyrithione's antifungal action is particularly beneficial. It reduces the yeast population on the skin, thereby alleviating the symptoms associated with its overgrowth, such as flaking, irritation, and redness.
Its efficacy in treating seborrheic dermatitis is attributed to its ability to reduce the Malassezia count, diminish inflammatory responses, and soothe the skin. Similarly, in dandruff, which is often linked to an excess of Malassezia, zinc pyrithione effectively reduces flaking and itchiness, promoting a healthier scalp environment.
The efficacy of zinc pyrithione in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff is well-documented. Its safety profile and efficacy have been confirmed by numerous studies, with significant improvements observed in both scalp and skin conditions following regular use.
Physiological Effects
- Antifungal Activity: It is effective against a range of fungi, including those that cause dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. Zinc Pyrithione inhibits the division of fungal cells, reducing their proliferation.
- Antibacterial Properties: This compound also exhibits antibacterial activity, making it useful in treating and preventing bacterial skin infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Zinc Pyrithione can reduce inflammation, which is beneficial in alleviating symptoms of various inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps in regulating sebum production, which can be beneficial for oily skin and conditions like acne.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis: Zinc Pyrithione is a common ingredient in anti-dandruff shampoos and is effective in controlling the flaking and itching associated with these conditions.
- Psoriasis: It can help manage the symptoms of psoriasis, particularly in reducing scaling and redness.
- Acne: Due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, Zinc Pyrithione can be beneficial in the treatment of acne.
- Fungal Infections: It is effective in treating various fungal skin infections due to its antifungal properties.
References
- Warshaw, E. M., et al. (2005). Efficacy of Zinc Pyrithione in Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff. Dermatology.
- Pierard-Franchimont, C., et al. (2002). Antidandruff shampoo efficacy in dandruff/seborrhoeic dermatitis. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Scheman, A., et al. (2000). Antimicrobial Activity of Zinc Pyrithione. American Journal of Infection Control.






SIZE: 30 mL

Unclog Pores

↓ Sebum

Anti-Acne

↓ inflammation

anti-aging
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid, a renowned beta hydroxy acid (BHA), is a cornerstone in dermatology and skincare due to its exceptional keratolytic and comedolytic properties. Its unique ability to penetrate oil-laden hair follicle pores makes it particularly effective in treating acne-prone and oily skin types.
Salicylic acid dissolves skin debris (sebum and dead skin cells) that clogs pores and causes acne. It's a mild antibacterial and powerful anti-inflammatory agent that helps reduce the redness and swelling associated with breakouts.
What sets salicylic acid apart in dermatological treatments is its ability to exfoliate the skin, not just on the surface but within the pores themselves. This is due to its oil-soluble nature, which allows it to penetrate deep into the pores and dissolve the keratin plugs that lead to blackheads and whiteheads.
Furthermore, salicylic acid also has the capacity to adjust the pH of the skin, creating an environment less favorable for the growth of acne-causing bacteria. Salicylic acid's efficacy in treating various skin conditions, particularly acne, has been extensively documented in the scientific literature. Studies have consistently shown its ability to reduce acne lesions in terms of count and severity. Additionally, salicylic acid is highly recommended for its effectiveness in treating other skin conditions, such as psoriasis and dandruff, due to its ability to soften and remove scales and flakes from the skin.
Physiological Effects
- Keratolytic Action: Salicylic acid is known for its ability to exfoliate the skin by dissolving the intercellular 'glue' that holds skin cells together, helping to remove dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- Comedolytic Effect: It is particularly effective in reducing comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) by unclogging pores and preventing the formation of new comedones.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Salicylic acid reduces inflammation, which is beneficial in treating acne and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps to regulate oil production, making it a valuable ingredient for managing oily and acne-prone skin.
- Penetration Enhancement: Due to its lipophilic nature, it can penetrate sebum-filled follicles, effectively treating acne located deep within the pores.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne Vulgaris: Salicylic acid is a cornerstone in acne treatment, effectively preventing and treating existing acne lesions.
- Psoriasis: Its keratolytic properties make it helpful in softening and removing scales associated with psoriasis.
- Warts: Salicylic acid is commonly used to treat warts because it can exfoliate and remove thick skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: It helps manage seborrheic dermatitis by reducing scaling and redness.
- Keratosis Pilaris: Salicylic acid can aid in smoothing the rough bumps associated with peratosis Pilaris.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 3, 135.
- Zander, E., & Weisman, S. (1992). Treatment of acne vulgaris with salicylic acid pads. Clinical Therapeutics.
- Gupta, A. K., & Nicol, K. (2004). The use of sulfur in dermatology. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
Zinc PCA
Zinc PCA, also known as Zinc Pyrrolidone Carboxylic Acid, is a skin care ingredient that combines the mineral zinc with a hydrating molecule PCA (Pyrrolidone Carboxylic Acid). It is renowned for its numerous benefits in skincare, particularly for its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and sebum-regulating properties.
Zinc PCA is derived from zinc, an essential mineral known for its antioxidant and skin-soothing capabilities. Zinc is also noted for its role in wound healing and its ability to reduce inflammation, which can be particularly beneficial for acne-prone and irritated skin. The PCA component is a natural moisturizing factor (NMF) found in the skin, which helps maintain the skin's hydration levels.
One of the key benefits of Zinc PCA is its ability to regulate sebum production. Excess sebum can lead to acne and oily skin, and Zinc PCA helps to moderate this by inhibiting the activity of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which is involved in oil production. This makes it an effective ingredient in formulations targeting oily and acne-prone skin (Schueller, R. and Romanowski, P., 2003).
In addition to its sebum-regulating properties, Zinc PCA possesses antimicrobial properties, which further contribute to its efficacy in treating acne. By reducing the presence of acne-causing bacteria on the skin, it helps to prevent and reduce acne breakouts.
Moreover, Zinc PCA's anti-inflammatory properties make it beneficial for soothing irritated skin and reducing redness and inflammation associated with various skin conditions, including acne, rosacea, and eczema.
Physiological Effects
- Sebum Regulation: Zinc PCA reduce and regulate sebum secretion and production, making it beneficial for oily and acne-prone skin by controlling excess oil production.
- Antimicrobial Action: Zinc has antimicrobial properties, particularly effective against acne-causing bacteria, reducing acne breakouts.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Zinc PCA reduces inflammation, which is beneficial in treating inflammatory skin conditions like acne and rosacea.
- Moisture Retention: PCA is a natural moisturizing factor (NMF) that helps maintain skin hydration, enhancing the skin’s moisture retention capabilities.
- Wound Healing: Zinc is essential for wound healing processes, aiding in the repair and regeneration of skin tissues.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne Management: Its ability to regulate sebum production and provide antimicrobial action makes Zinc PCA a valuable ingredient in acne treatments.
- Oily Skin: It's beneficial in controlling excess oiliness and maintaining a balanced skin environment.
- Sensitive Skin Conditions: Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, Zinc PCA soothes sensitive skin and conditions like rosacea.
- Skin Hydration: Its role as an NMF helps in maintaining skin hydration, useful in treating dry skin conditions.
References
- Schagen, S. K., et al. (2012). Discovering the link between nutrition and skin aging. Dermato-endocrinology.
- Firooz, A., et al. (2011). Zinc therapy in dermatology: a review. Dermatology Research and Practice.
- Gupta, M., et al. (2014). Zinc therapy in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal.
- Schueller, R. and Romanowski, P. (2003). Conditioning Agents for Hair and Skin. Cosmetic Science and Technology Series. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, USA.
Retinoic acid analogue
Retinoic acid, often referred to as tretinoin in its pharmaceutical form, is the active form of Vitamin A. It is widely recognized for its powerful effects in dermatology and skin care, particularly in treating acne and signs of skin aging.
Retinoic acid works at the cellular level to modify gene expression and affect cell growth. In treating acne, it promotes the turnover of skin cells, reducing the likelihood of pore-clogging and helping to clear existing breakouts. Additionally, it decreases the cohesiveness of follicular epithelial cells, further preventing the formation of comedones.
Retinoic acid's ability to stimulate collagen production is a key benefit in anti-aging skincare. This leads to a reduction in fine lines and wrinkles and an improvement in overall skin texture and tone. It also aids skin discoloration and hyperpigmentation by accelerating cell turnover, bringing new skin cells to the surface faster, and shedding pigmented and damaged cells.
Despite its benefits, retinoic acid can irritate the skin, causing side effects like redness, dryness, and peeling, especially during the initial period of use. Its potency means it is generally available by prescription and requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional.
Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) is a newer, esterified form of retinoic acid. Unlike cosmetic retinol, HPR binds directly to the retinoid receptors of the skin cells without needing conversion. This direct binding allows it to deliver similar benefits to retinoic acid, such as stimulating collagen production, improving skin elasticity, and reducing signs of aging, but with a lower risk of irritation.
HPR is considered more gentle and less irritating than traditional retinoic acid while offering comparable benefits. With HPR, everyone has access to the benefits of prescription retinoids without the risk of side effects.
Physiological Effects
- Cell Turnover and Renewal: HPR promotes rapid cell turnover, aiding in the exfoliation of dead skin cells and generating new cells.
- Skin Texture: Promoting cell renewal improves skin texture and addresses issues like roughness and dullness.
- Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improving skin elasticity.
- Acne Treatment: Effective in treating acne by unclogging pores and reducing the size of sebaceous glands, it diminishes both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions.
- Pigmentation: It can reduce hyperpigmentation by accelerating the turnover of hyperpigmented skin cells and inhibiting melanin production.
- Photoaging: Effective in treating signs of photoaging, reversing some of the damage caused by UV radiation.
Special Benefits
- Retinoid Receptor Activity: HPR, an ester of retinoic acid, binds directly to retinoid receptors in the skin, enabling it to work without needing to be converted into retinoic acid.
- Lower Irritation: Typically, it causes less irritation than retinoic acid, making it more suitable for sensitive skin types.
- Collagen Stimulation and Anti-Aging: Like retinoic acid, HPR helps in stimulating collagen production and has anti-aging properties.
- Acne and Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats acne and reduces hyperpigmentation, often with fewer side effects than retinoic acid.
- Stability and Penetration: HPR is more stable and lipid-soluble, so it penetrates the skin more effectively and is less prone to degradation.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., ... & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Fisher, G. J., Wang, Z. Q., Datta, S. C., Varani, J., Kang, S., & Voorhees, J. J. (1996). Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light. New England Journal of Medicine, 337(20), 1419-1428.
- Truchuelo, M. T., Jiménez, N., Jaén, P. (2018). Assessment of the efficacy of a new complex-based retinoic acid and retinol in a 3-month study using objective methods and skin biomarker analysis. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 17(3), 347-354.
- Mukherjee, S., et al. (2006). Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety. Clinical Interventions in Aging.
- Randhawa, M., et al. (2015). Hydroxypinacolone retinoate: a new retinoid and its use in dermatology. Skin Therapy Letter.






SIZE: 50 mL

Exfoliating

Smooth Skin

Ingrown hair

Anti-Acne

Anti-Aging
Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is highly acclaimed for its remarkable exfoliating and rejuvenating properties. Its small molecular size enables deep skin penetration, fostering efficient exfoliation at the cellular level.
Glycolic acid’s water solubility allows it to penetrate the upper layers of the skin easily. Its primary mechanism of action involves weakening the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their shedding, and revealing the newer, healthier skin beneath. This process of accelerated cell turnover is instrumental in addressing a range of skin concerns, from aging signs like fine lines and wrinkles to texture irregularities and hyperpigmentation.
Glycolic acid's efficacy extends beyond mere exfoliation. It's also recognized for stimulating collagen production, a crucial protein in maintaining skin's elasticity and firmness. This aspect contributes to its anti-aging benefits. Furthermore, its hydrating properties add to its appeal, as they help increase the skin's capacity to retain moisture, leading to a more supple and vibrant complexion.
Clinical studies have consistently supported glycolic acid's role in improving skin appearance. Research indicates significant improvements in skin texture and pigmentation and the visible reduction of wrinkles and fine lines with glycolic acid.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: Glycolic acid is a powerful exfoliant. It dissolves the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, facilitating their removal and revealing newer, healthier skin underneath.
- Increased Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for skin elasticity and firmness. This action helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Enhanced Skin Hydration: Glycolic acid improves the skin's ability to retain moisture, enhancing hydration and a more plump, vibrant skin appearance.
- Skin Brightening: Removing dead skin cells can brighten the complexion and reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Improved Skin Texture: Regular use of glycolic acid can lead to smoother, more even textured skin, making it beneficial for conditions like keratosis pilaris.
- Acne Treatment: Its exfoliating properties help in unclogging pores, thereby reducing the occurrence of acne breakouts.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Glycolic acid is widely used in anti-aging products to reduce signs of aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: It helps manage acne by exfoliating the skin and removing blockage from pores.
- Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats hyperpigmentation by accelerating the removal of hyperpigmented skin cells.
- Textural Irregularities: Glycolic acid can improve skin texture and is beneficial for treating keratosis pilaris and other conditions of rough skin.
- Sun-Damaged Skin: It helps rejuvenate sun-damaged skin by accelerating cell turnover and collagen synthesis.
References
- Bernstein, E. F. (2001). Glycolic acid treatment increases type I collagen mRNA and hyaluronic acid content of human skin. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Sharad, J. (2013). Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 35(3), 388-391.
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid, a renowned beta hydroxy acid (BHA), is a cornerstone in dermatology and skincare due to its exceptional keratolytic and comedolytic properties. Its unique ability to penetrate oil-laden hair follicle pores makes it particularly effective in treating acne-prone and oily skin types.
Salicylic acid dissolves skin debris (sebum and dead skin cells) that clogs pores and causes acne. It's a mild antibacterial and powerful anti-inflammatory agent that helps reduce the redness and swelling associated with breakouts.
What sets salicylic acid apart in dermatological treatments is its ability to exfoliate the skin, not just on the surface but within the pores themselves. This is due to its oil-soluble nature, which allows it to penetrate deep into the pores and dissolve the keratin plugs that lead to blackheads and whiteheads.
Furthermore, salicylic acid also has the capacity to adjust the pH of the skin, creating an environment less favorable for the growth of acne-causing bacteria. Salicylic acid's efficacy in treating various skin conditions, particularly acne, has been extensively documented in the scientific literature. Studies have consistently shown its ability to reduce acne lesions in terms of count and severity. Additionally, salicylic acid is highly recommended for its effectiveness in treating other skin conditions, such as psoriasis and dandruff, due to its ability to soften and remove scales and flakes from the skin.
Physiological Effects
- Keratolytic Action: Salicylic acid is known for its ability to exfoliate the skin by dissolving the intercellular 'glue' that holds skin cells together, helping to remove dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- Comedolytic Effect: It is particularly effective in reducing comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) by unclogging pores and preventing the formation of new comedones.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Salicylic acid reduces inflammation, which is beneficial in treating acne and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps to regulate oil production, making it a valuable ingredient for managing oily and acne-prone skin.
- Penetration Enhancement: Due to its lipophilic nature, it can penetrate sebum-filled follicles, effectively treating acne located deep within the pores.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne Vulgaris: Salicylic acid is a cornerstone in acne treatment, effectively preventing and treating existing acne lesions.
- Psoriasis: Its keratolytic properties make it helpful in softening and removing scales associated with psoriasis.
- Warts: Salicylic acid is commonly used to treat warts because it can exfoliate and remove thick skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: It helps manage seborrheic dermatitis by reducing scaling and redness.
- Keratosis Pilaris: Salicylic acid can aid in smoothing the rough bumps associated with peratosis Pilaris.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 3, 135.
- Zander, E., & Weisman, S. (1992). Treatment of acne vulgaris with salicylic acid pads. Clinical Therapeutics.
- Gupta, A. K., & Nicol, K. (2004). The use of sulfur in dermatology. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.






SIZE: 50 mL

Antioxidant

anti-aging

DNA repair

sun protection

Moisturizing
Coenzyme Q10
CoQ10 is a potent ingredient that offers comprehensive skin health and appearance benefits. Its role in energy production and its antioxidant and anti-aging properties make it invaluable for photoprotection, anti-aging, and overall skin vitality. Its incorporation into DermExcel sunscreen represents a holistic approach to skin health, addressing protective and restorative needs.
Physiological Impact
- Skin Barrier Enhancement: CoQ10 contributes to the strength and health of the skin barrier, improving its ability to retain moisture and protect against external irritants and pollutants.
- Skin Repair and Regeneration: It supports the skin's natural ability to repair itself and regenerate, maintaining a healthy, youthful appearance. This is particularly beneficial in mature skin, where natural levels of CoQ10 may be depleted.
Pharmacological Advantages
- Anti-Aging Effects: CoQ10's antioxidant properties contribute to its anti-aging effects. By reducing oxidative stress, it helps to minimize the visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles and fine lines.
- Photoprotection: It enhances the skin's defense against photoaging caused by exposure to UV rays. CoQ10 helps to mitigate the degradation of collagen and elastin, proteins essential for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness.
Biochemical Benefits
- Cellular Energy Production: CoQ10 plays a crucial role in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, which is essential for the production of ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell. This function is vital for maintaining the health and vitality of skin cells.
- Antioxidant Properties: It acts as a lipophilic antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and preventing oxidative damage to cell membranes, proteins, and DNA. This is particularly important in the skin, which is frequently exposed to oxidative stress from environmental factors like UV radiation.
Vitamin E
The fat-soluble Vitamin E's benefits in maintaining skin health and appearance are well-acknowledged in both cosmetic and clinical dermatology. Comprising a group of eight compounds, including four tocopherols and four tocotrienols, Vitamin E is known for its role in protecting cell membranes from oxidative damage.
Vitamin E is celebrated in skincare for its ability to neutralize free radicals caused by environmental stressors such as UV radiation and pollution. These free radicals can lead to premature skin aging, making Vitamin E a valuable ingredient in anti-aging skincare products. Its antioxidant action helps to protect the skin from damage, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and improve skin texture and tone.
Additionally, Vitamin E is known for its moisturizing benefits. It helps to strengthen the skin barrier, reduce moisture loss, and keep the skin hydrated and supple. This makes it especially beneficial for dry and damaged skin.
Vitamin E also has anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial in soothing and calming irritated skin. This has implications for conditions such as dermatitis and acne, where inflammation plays a key role.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Protection: Vitamin E neutralizes harmful free radicals in the skin, preventing oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
- Moisturization: It has moisturizing properties, helping to improve skin hydration and alleviate dryness.
- Wound Healing: Vitamin E may assist in the skin's healing process, although its efficacy in wound healing is still a subject of research.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it can provide some degree of photoprotection by strengthening the skin's defense against UV-induced damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: It helps reduce skin inflammation and is beneficial in managing conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Its antioxidant properties make it useful in anti-aging skincare products to protect against free radical damage and improve skin appearance.
- Dry Skin Conditions: Vitamin E's moisturizing effects are beneficial in treating dry skin and improving overall skin texture.
- Inflammatory Skin Diseases: It can be helpful in soothing inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
- Sun Protection and Repair: Vitamin E is included in sunscreens and after-sun products for its ability to mitigate sun damage.
- Scar Treatment: Some studies suggest Vitamin E may help reduce the appearance of scars, although evidence is mixed.
References
- Thiele, J. J., Hsieh, S. N., & Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S. (1998). Vitamin E: Critical Review of Its Current Use in Cosmetic and Clinical Dermatology. Dermatologic Surgery, 24(7), 805–813.
- Ratz-Łyko, A., & Arct, J. (2016). Anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties of active skin care ingredients. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 9(9), 36–40.
- Keen, M. A., & Hassan, I. (2016). Vitamin E in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal.
- Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S., & Thiele, J. (2007). Vitamin E in human skin: Organ-specific physiology and considerations for its use in dermatology. Molecular Aspects of Medicine.
- Nachbar, F., & Korting, H. C. (1995). The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin. Journal of Molecular Medicine.
Broad Spectrum Filters
Tinosorb® M and Tinosorb® S represent sophisticated advancements in sun protection technology.
Tinosorb® M
- Biochemical Action: A unique UV filter due to its ability to function through absorption, reflection, and scattering of UV rays.
- Physiological Impact: The triple-action mechanism of Tinosorb® M offers comprehensive sun protection. By mitigating the penetration of both UVA and UVB rays, it significantly reduces the risk of DNA damage, photoaging, and carcinogenesis. Its ability to remain on the skin's surface reduces systemic exposure, making it a safer option with minimal potential for irritation or allergic reactions.
Tinosorb® S
- Biochemical Action: A broad-spectrum UV filter with a molecular structure that effectively absorbs both UVA and UVB rays. Additionally, it enhances the photostability of other UV filters, making the sunscreen formulation more effective over time.
- Physiological Impact: By providing extensive UVA and UVB protection, Tinosorb® S plays a crucial role in preventing short-term sun damage like sunburn and long-term risks such as skin aging and skin cancer. Its photostability ensures sustained protection during sun exposure, and its compatibility with other UV filters means it can be used to formulate sunscreens that are both effective and suitable for sensitive skin.
Sunscreen
Using sunscreen is a fundamental aspect of skin care and preventive dermatology. It's essential for reducing the risk of skin cancers and photoaging and maintaining overall skin health in the face of constant exposure to UV radiation.
Sunscreen is a vital skincare product designed to protect the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Two primary types of UV radiation affect the skin: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and are primarily responsible for aging and long-term skin damage, whereas UVB rays cause sunburn and play a key role in developing skin cancer.
Sunscreen products work by either absorbing, reflecting, or scattering sunlight. They contain chemical compounds that absorb UV radiation and convert it into a small amount of heat or physical compounds (like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) that act as a physical barrier, reflecting UV light away from the skin.
The effectiveness of sunscreen is measured by its Sun Protection Factor (SPF). SPF indicates how well the sunscreen protects against UVB rays. For example, an SPF of 30 means it would take 30 times longer for your skin to burn than without sunscreen. However, it's important to note that no sunscreen can block 100% UV rays.
Regular use of sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 can reduce the risk of skin cancer, prevent sunburn, and slow down the skin's aging process.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Prevention of Sunburn: Sunscreen protects the skin from UVB rays, which cause sunburn. This reduces the immediate risk of skin damage and discomfort.
- Skin Cancer Prevention: Regular use of sunscreen significantly lowers the risk of developing various types of skin cancer, especially melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma.
- Prevention of Photoaging: Sunscreen also shields the skin from UVA rays, which penetrate deeper into the skin and are primarily responsible for photoaging, including wrinkles, leathery skin, and sunspots.
- Protection Against Photosensitivity: Sunscreen helps prevent flare-ups triggered by sun exposure for individuals with photosensitive skin conditions like lupus or rosacea.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: It aids in preventing and managing hyperpigmentation and melasma, conditions exacerbated by sun exposure.
- General Skin Health: Sunscreen helps maintain overall skin health and integrity by protecting the skin from UV damage.
References
- Burnett, M. E., & Wang, S. Q. (2011). Current sunscreen controversies: a critical review. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine.
- Green, A. C., et al. (2011). Reduced melanoma after regular sunscreen use: randomized trial follow-up. Journal of Clinical Oncology.
- Hughes, M. C. B., et al. (2013). Sunscreen and Prevention of Skin Aging: A Randomized Trial. Annals of Internal Medicine.