your dermal diagnosis™ results
Good day

's Dermal Diagnosis™ Profile





YOUR SKIN'S MAIN CHARACTERISTICS

Allergy Prone

Pigmentation

↑ Sebum

Aging skin

hydrated skin

skincare awareness

Allergy Prone

Pigmentation

Oil Management

Aging skin
Aging . Oily . Pigmentation . Allergy
treatment objectives





↓ pigmentation

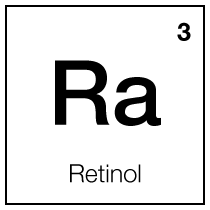
DNA repair

smooth skin

anti-aging

↑ Elasticity






Choose options




Aging . Oily . Pigmentation . Allergy
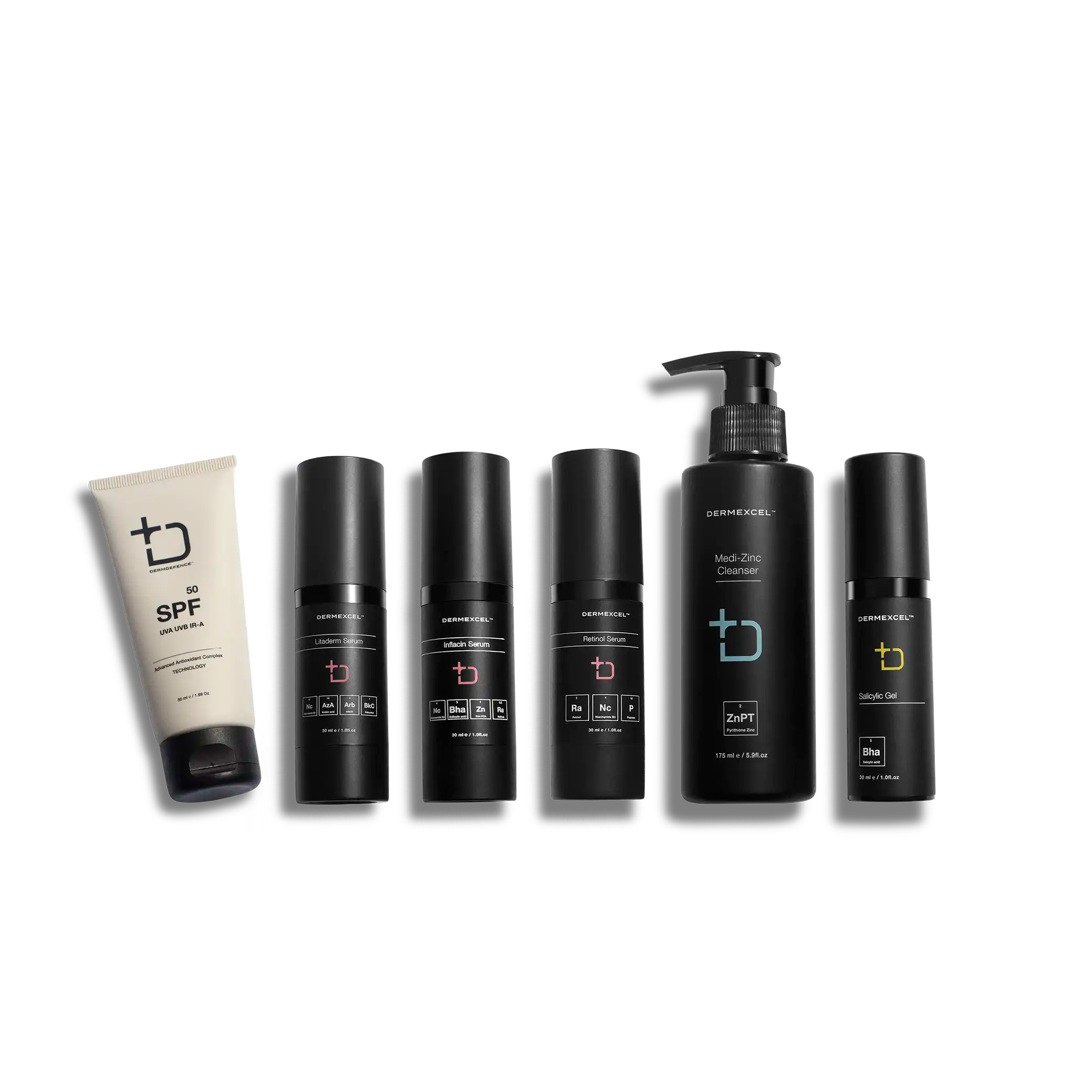
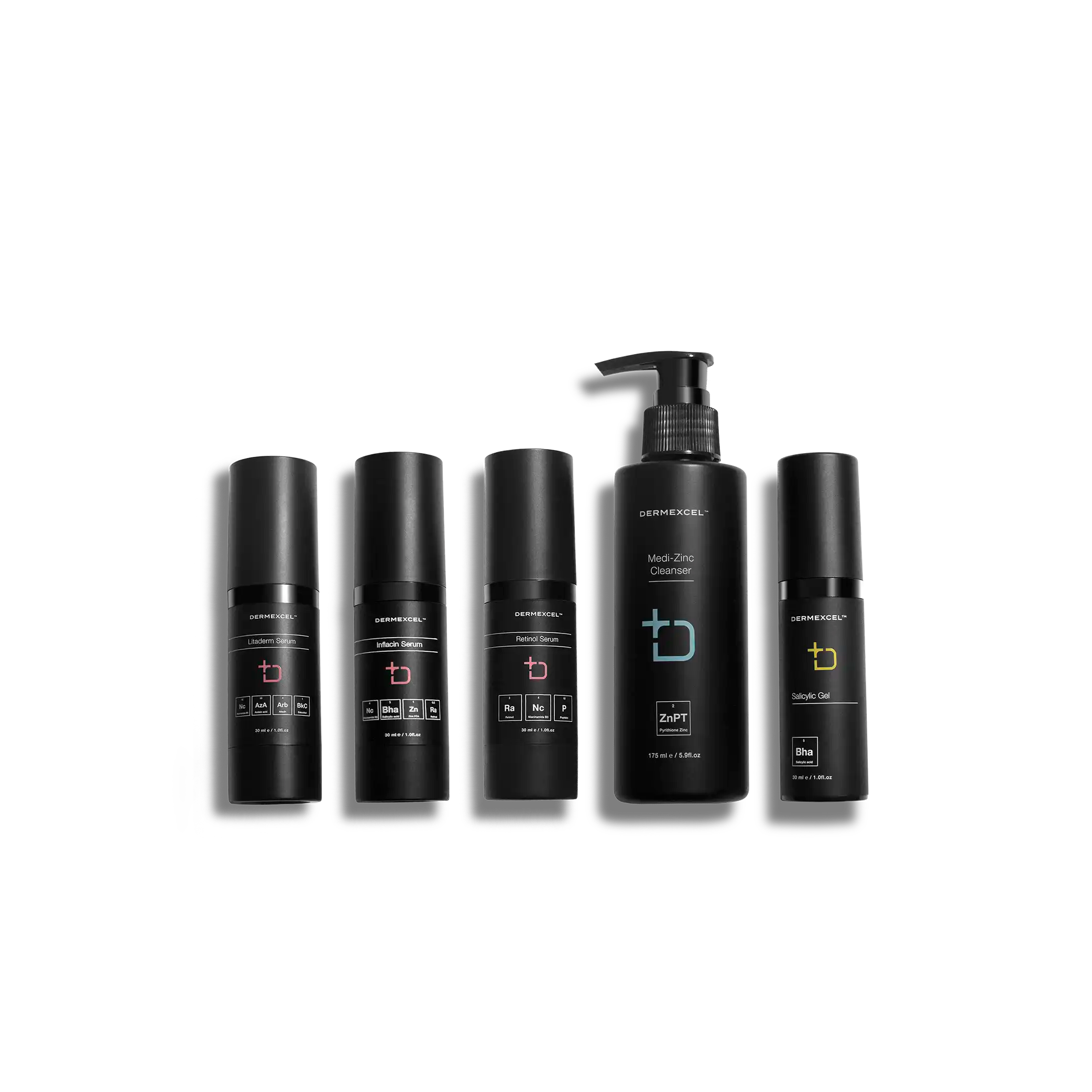
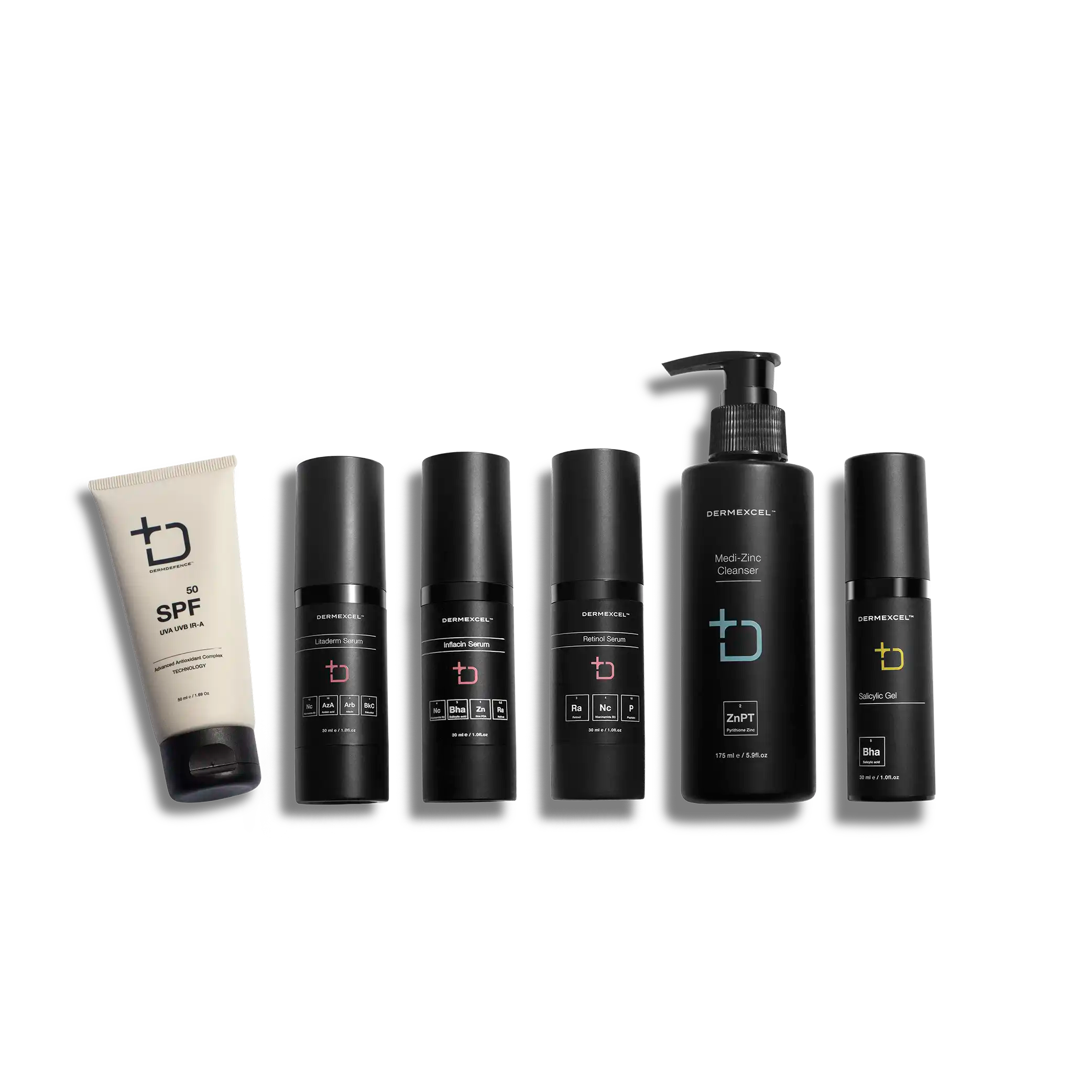
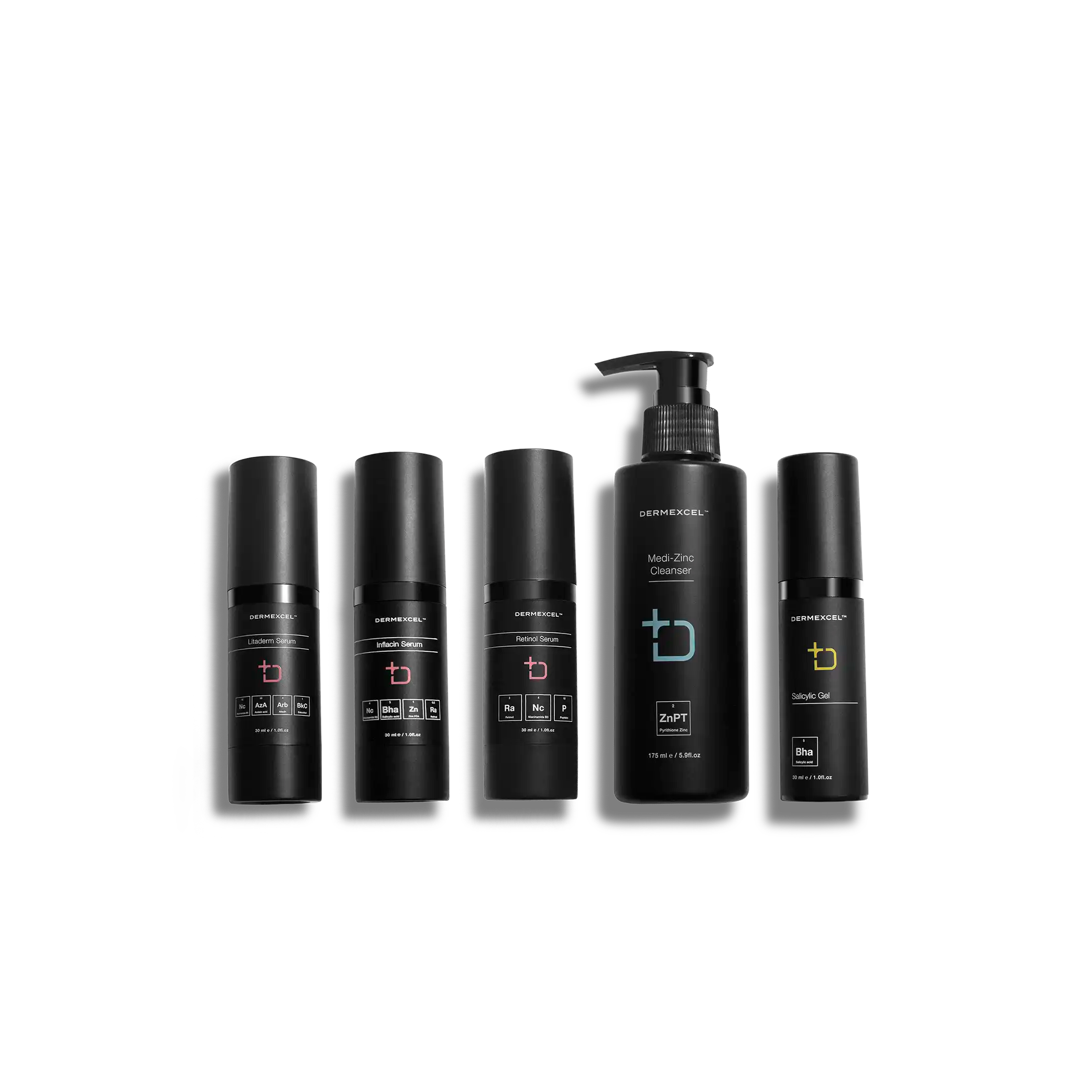
products in your treatment pack
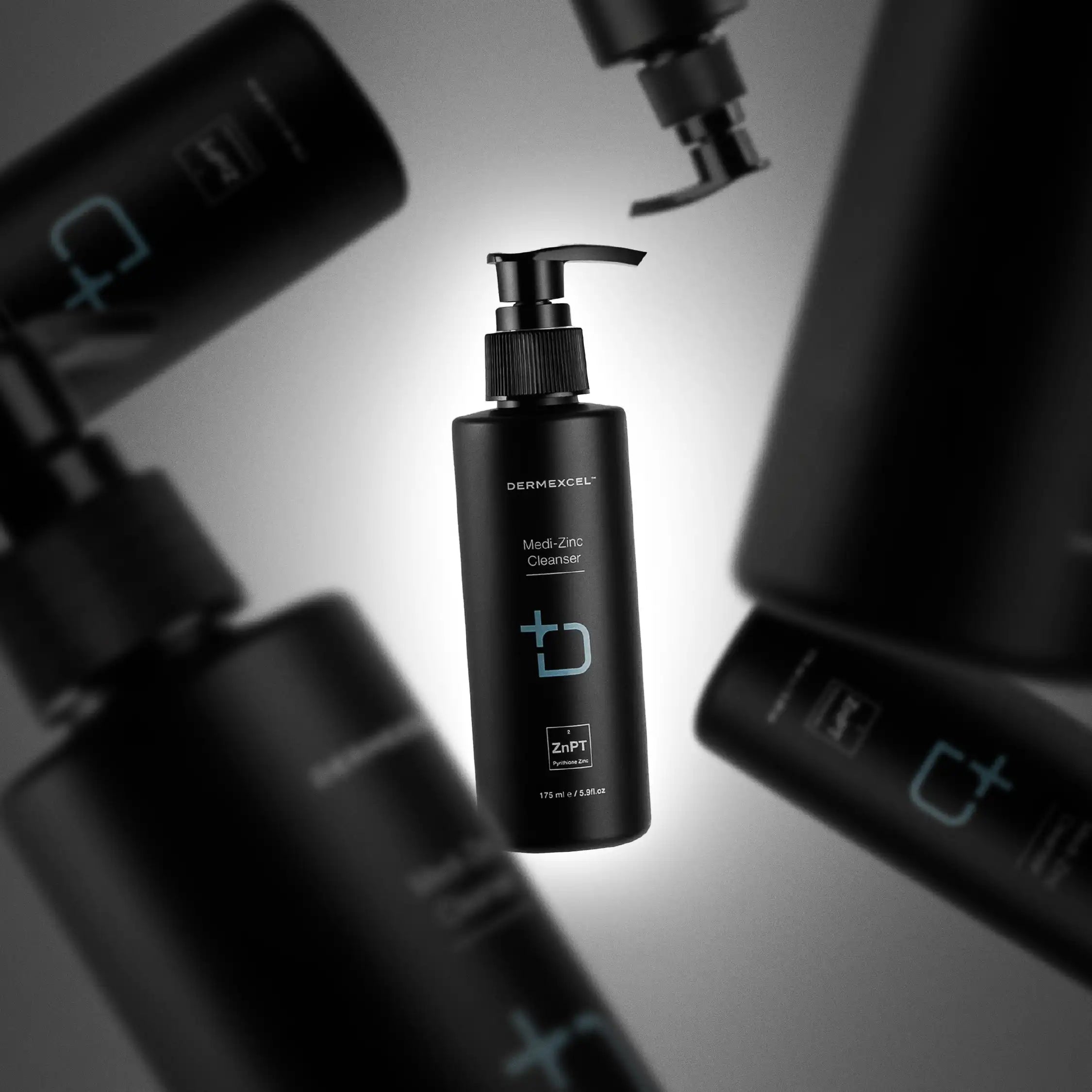



SIZE: 100 mL

Itch Relief

Anti-Acne

↓ inflammation

anti-redness

Anti-microbial





SIZE: 30 mL

Unclog Pores

↓ Sebum

Anti-Acne

↓ inflammation

anti-aging
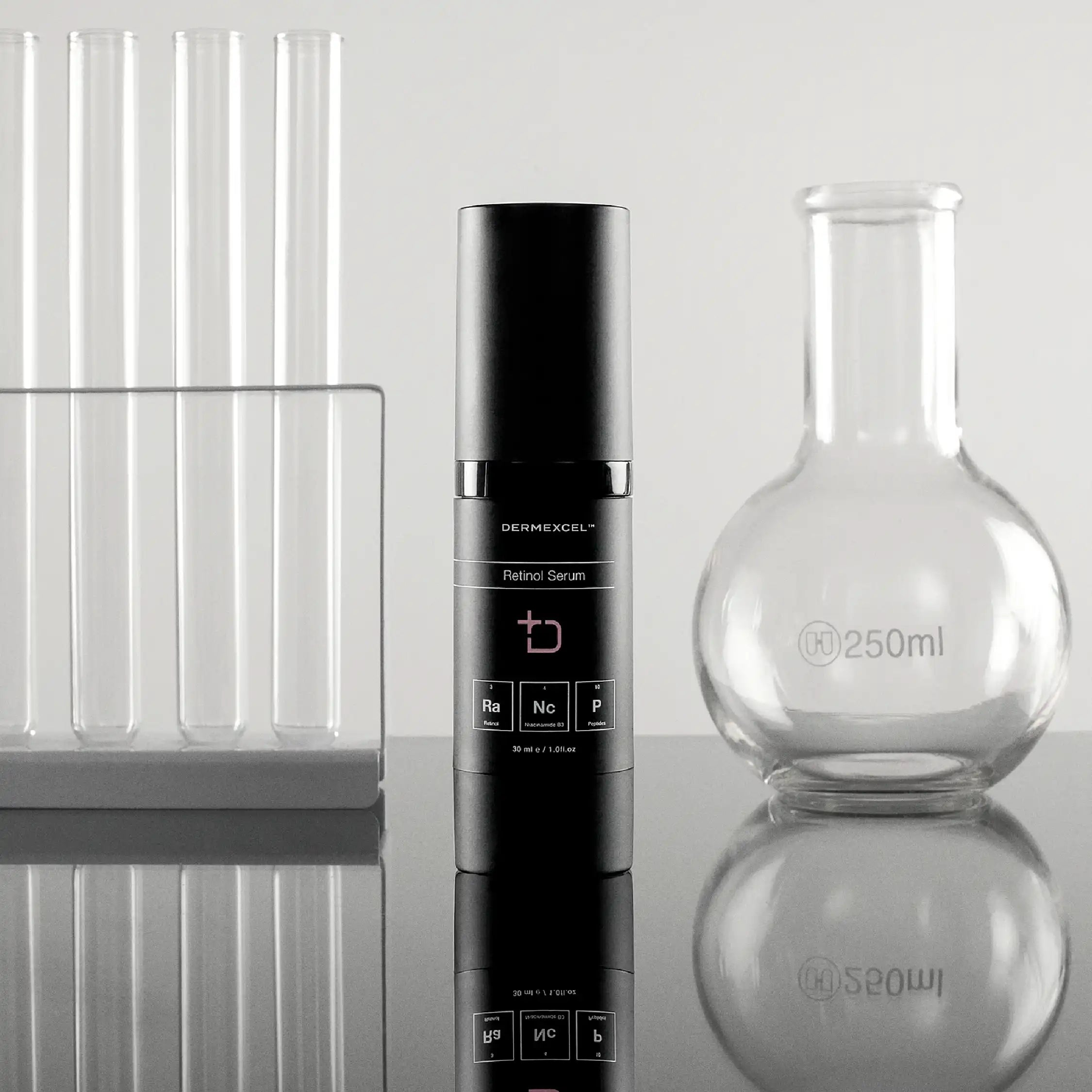






SIZE: 30 mL

Unclog Pores

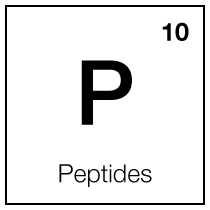
Minimize Pores

Smooth Skin

anti-aging

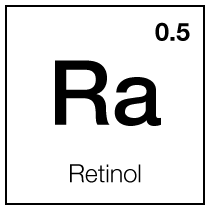
DNA repair





SIZE: 30 mL

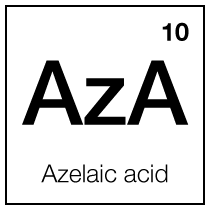
Even Skin Tone

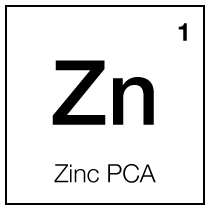
Moisturizing

anti-redness

anti-aging

↓ inflammation









SIZE: 30 mL

↓ Sebum

Unclog Pores

Anti-Acne

↓ inflammation

Ingrown hair






SIZE: 50 mL

Antioxidant

anti-aging

DNA repair

sun protection

Moisturizing