your dermal diagnosis™ results
Good day,
We're thrilled you're taking proactive steps to understand your skin better.
Below, you'll find your most recent Dermal Diagnosis™ results. Use this data as a roadmap to achieving healthier skin.
| Date | Dermal Diagnosis™ | Profile and Treatment Plan |
|---|---|---|
DERMAL DIAGNOSIS™ RESULT BREAKDOWN
| Aging Score | Hydration Score | Pigmentation Score | Inflammation category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Dermal Diagnosis™ |
|---|---|
DERMAL DIAGNOSIS™ RESULT BREAKDOWN
| Aging Score | |
| Hydration Score | |
| Pigmentation Score | |
| Inflammation category |

's Dermal Diagnosis™ Profile:
Aging Skin with Pigmentation
your frustrations
- Enlarged pores.
- Premature skin aging.
- Uneven skin tone with dark spots or patches.
your goals
- Minimized pores.
- Prevention and correction of premature skin aging including lines and wrinkles.
- Radiant and healthy skin with an even skin tone.
- Radiant skin with an even skin tone.
- Smooth skin texture.

hydrated skin

resilient skin

luminous skin

no inflammation
-
Natural Hydration: Your oily skin provides a natural layer of hydration, forming a protective barrier against environmental damage. This helps to keep the skin plump and potentially reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
-
Luminous Complexion: The natural sheen associated with oily skin can give the complexion a healthy-looking glow, contributing to a more vibrant appearance.
-
Antioxidant Protection: Oily skin sebum contains vitamin E, an antioxidant that can offer some degree of protection against external pollutants and oxidative stress.
-
No Acne Breakouts: Despite being oily, this skin type does not experience acne breakouts, a common concern for many with oily skin. This can simplify skincare routines and reduce the need for harsh acne treatments that exacerbate sensitivity or aging concerns.

Aging skin

Oil Management

Pigmentation
-
Pore Congestion: The excess oil production can lead to enlarged pores and increase the likelihood of blackheads, whiteheads, and acne, which can be challenging to manage alongside aging skin concerns.
-
Hydration Balance: Ensuring the skin is adequately hydrated without adding to its natural oiliness requires carefully selecting moisturizing ingredients that provide hydration and support the skin barrier without feeling heavy or greasy.
-
Hyperpigmentation: Issues such as uneven skin tone, dark spots, and melasma are prominent and require consistent management and treatment.
-
Aging Skin: While oily skin may be more resilient to the formation of fine lines and wrinkles, addressing other signs of aging, such as loss of firmness or elasticity, can be complicated by the need to also manage oiliness and enlarged pores.
Aging Skin with Pigmentation
Treatment objectives

Smooth skin texture
Replace dull and dead skin cells with remodeled skin layers. Resurfacing procedures can induce new collagen formation with a more structured pattern.

DNA Protection and Repair
Safeguard and repair UV-induced DNA damage, utilizing a blend of UV defense, Retinol, Niacinamide, and antioxidants. This strategy prevents future damage and aids in the repair of existing cellular impairments.

Inhibit hyperpigmentation
Inhibit the pathways in the hyperpigmentation process to stop the stimulation, production and transfer of melanin (pigment cells).

Prevent & Repair Premature Aging
Protect the skin from factors that accelerate aging, such as UV exposure and pollution, and correct existing signs of aging, like fine lines, wrinkles, and loss of elasticity.
Aging Skin with Pigmentation
Beneficial Active Ingredients
Peptides
Peptides are short chains of amino acids with a wide range of biological functions and skin benefits. They are essentially small fragments of proteins, which are fundamental components of all living cells, including collagen and elastin in the skin.
In skincare, peptides are known for enhancing skin repair and rejuvenation. They function as signaling molecules, instructing cells to perform specific tasks such as producing collagen and elastin, vital for maintaining the skin's firmness and elasticity. This makes peptides especially beneficial in anti-aging products, as they can help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Research has shown that certain peptides can improve skin barrier function, increase hydration, and soothe skin inflammation. This makes them suitable for products targeting dry, sensitive, or inflamed skin.
Peptides, with their diverse functions in promoting collagen production, strengthening the skin barrier, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory actions, are pivotal in managing various dermatological conditions, particularly in anti-aging, sensitive skin care, and wound healing applications.
Physiological Effects
- Collagen Production: Certain peptides, known as signal peptides, stimulate collagen production in the skin, enhancing skin firmness and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Barrier Strengthening: Peptides can strengthen the skin barrier, improve hydration, and protect against environmental damage.
- Wound Healing: Some peptides play a role in the skin's natural healing process, aiding tissue repair and regeneration.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Certain peptides have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to soothe and calm irritated skin.
- Antimicrobial Action: Some peptides possess antimicrobial properties, potentially helping to manage acne and other skin infections.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Peptides can stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity.
- Sensitive Skin Conditions: Peptides are beneficial for sensitive or inflamed skin due to their soothing properties.
- Acne-Prone Skin: Antimicrobial peptides can be effective in acne treatment formulations.
- Wound Care and Repair: Peptides improve wound healing and reduce scarring.
References
- Gorouhi, F., & Maibach, H. I. (2009). Role of topical peptides in preventing or treating aged skin. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Schagen, S. K. (2012). Topical peptide treatments with effective anti-aging results. Cosmetics.
- Varani, J., et al. (2001). Vitamin A antagonizes decreased cell growth and elevated collagen-degrading matrix metalloproteinases and stimulates collagen accumulation in naturally aged human skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Bakuchiol
Bakuchiol's mechanism of action is similar to retinol's; it stimulates collagen production and accelerates cell turnover, improving skin texture and tone. It also helps reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation, making it an effective ingredient in anti-aging skincare products.
One of the key advantages of bakuchiol over traditional retinol is its gentleness on the skin. Retinol is known for potential side effects like dryness, redness, and irritation, particularly in sensitive skin or when used in high concentrations. Bakuchiol, however, is far less irritating. In addition to its anti-aging properties, bakuchiol exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, further contributing to its skin benefits. It helps protect the skin from oxidative stress and can soothe it, reducing redness and inflammation.
Bakuchiol's retinol-like effects and its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties make it an effective ingredient for various skin concerns, especially for those seeking natural alternatives in anti-aging and acne treatment.
Physiological Effects
- Retinol-like Function: Bakuchiol mimics the actions of retinol, stimulating collagen production. This helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improves skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Properties: It offers antioxidant benefits, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Bakuchiol has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help soothe the skin and reduce redness and irritation.
- Improved Skin Tone and Texture: Regular use of bakuchiol can improve skin tone and texture, making it smoother and more even.
- Acne Management: Bakuchiol's antibacterial properties and ability to regulate sebum production make it effective in managing acne.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Bakuchiol is popular in anti-aging skincare because it stimulates collagen production and reduces signs of aging.
- Sensitive Skin: As a gentler alternative to retinol, it is suitable for sensitive skin types that cannot tolerate traditional retinoids.
- Acne-Prone Skin: Its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties are beneficial in acne treatments.
- Hyperpigmentation: Bakuchiol can help treat hyperpigmentation, enhance skin radiance, and reduce dark spots.
References
- Chaudhuri, R. K., & Bojanowski, K. (2014). Bakuchiol: a retinol-like functional compound revealed by gene expression profiling and clinically proven to have anti-aging effects. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Dhaliwal, S., et al. (2019). Prospective, randomized, double-blind assessment of topical bakuchiol and retinol for facial photoageing. British Journal of Dermatology.
- Sivamani, R. K., et al. (2019). Clinical efficacy of a bakuchiol, niacinamide and zinc pyrithione formulation in facial sebum control and mild acne. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is highly acclaimed for its remarkable exfoliating and rejuvenating properties. Its small molecular size enables deep skin penetration, fostering efficient exfoliation at the cellular level.
Glycolic acid’s water solubility allows it to penetrate the upper layers of the skin easily. Its primary mechanism of action involves weakening the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their shedding, and revealing the newer, healthier skin beneath. This process of accelerated cell turnover is instrumental in addressing a range of skin concerns, from aging signs like fine lines and wrinkles to texture irregularities and hyperpigmentation.
Glycolic acid's efficacy extends beyond mere exfoliation. It's also recognized for stimulating collagen production, a crucial protein in maintaining skin's elasticity and firmness. This aspect contributes to its anti-aging benefits. Furthermore, its hydrating properties add to its appeal, as they help increase the skin's capacity to retain moisture, leading to a more supple and vibrant complexion.
Clinical studies have consistently supported glycolic acid's role in improving skin appearance. Research indicates significant improvements in skin texture and pigmentation and the visible reduction of wrinkles and fine lines with glycolic acid.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: Glycolic acid is a powerful exfoliant. It dissolves the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, facilitating their removal and revealing newer, healthier skin underneath.
- Increased Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for skin elasticity and firmness. This action helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Enhanced Skin Hydration: Glycolic acid improves the skin's ability to retain moisture, enhancing hydration and a more plump, vibrant skin appearance.
- Skin Brightening: Removing dead skin cells can brighten the complexion and reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Improved Skin Texture: Regular use of glycolic acid can lead to smoother, more even textured skin, making it beneficial for conditions like keratosis pilaris.
- Acne Treatment: Its exfoliating properties help in unclogging pores, thereby reducing the occurrence of acne breakouts.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Glycolic acid is widely used in anti-aging products to reduce signs of aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: It helps manage acne by exfoliating the skin and removing blockage from pores.
- Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats hyperpigmentation by accelerating the removal of hyperpigmented skin cells.
- Textural Irregularities: Glycolic acid can improve skin texture and is beneficial for treating keratosis pilaris and other conditions of rough skin.
- Sun-Damaged Skin: It helps rejuvenate sun-damaged skin by accelerating cell turnover and collagen synthesis.
References
- Bernstein, E. F. (2001). Glycolic acid treatment increases type I collagen mRNA and hyaluronic acid content of human skin. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Sharad, J. (2013). Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 35(3), 388-391.
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan found throughout the body's connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. Most abundantly present in the skin, eyes, and synovial fluid, HA is renowned for its exceptional capacity to retain moisture — a single gram can hold up to six liters of water.
In skincare, the primary appeal of hyaluronic acid lies in its unparalleled hydrating abilities. As a humectant, HA attracts and retains moisture from the environment, providing intense hydration to the skin. This hydrating property contributes significantly to maintaining skin plumpness, suppleness, and elasticity.
Beyond hydration, hyaluronic acid also plays a vital role in skin repair and regeneration. It supports the skin's healing and repair processes, and its anti-inflammatory properties help calm irritated skin. Moreover, HA's ability to promote collagen production, a crucial protein for skin elasticity, further underscores its anti-aging benefits.
The molecular size of hyaluronic acid influences its skin penetration and efficacy. High-molecular-weight HA remains on the skin's surface, providing hydration and forming a barrier against moisture loss. In contrast, low-molecular-weight HA penetrates deeper into the skin's layers, offering more profound hydrating and rejuvenating effects.
Hyaluronic acid's remarkable ability to hydrate, improve skin elasticity, aid in wound healing, and provide antioxidant protection makes it valuable in managing various dermatological conditions, particularly aging, dryness, and sensitive skin.
Physiological Effects
- Hydration: Hyaluronic acid is a powerful humectant that can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water, significantly enhancing skin hydration and leading to plumper, more hydrated skin.
- Skin Elasticity and Wrinkle Reduction: By increasing skin moisture, it improves skin elasticity, reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and gives the skin a more youthful appearance.
- Wound Healing: It plays a role in wound healing due to its ability to regulate inflammation levels and signal the body to build more blood vessels in the damaged area.
- Barrier Enhancement: Hyaluronic acid helps reinforce the skin's natural barriers, protecting against environmental factors and retaining moisture.
- Antioxidant Properties: It provides antioxidant defense against free-radical damage from the sun and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Its ability to reduce wrinkles and improve skin elasticity makes it popular in anti-aging skincare products.
- Dry Skin: Hyaluronic acid is beneficial in treating dry skin conditions by providing intense hydration.
- Wound Care: Its role in wound healing is leveraged in post-procedure care, such as after laser treatments, and in healing minor cuts and abrasions.
- Acne Scars: It can help treat acne scars by promoting skin regeneration and reducing inflammation.
- Sensitive Skin: Hyaluronic acid is suitable for sensitive skin due to its gentle nature. It provides hydration without irritating.
References
- Papakonstantinou, E., Roth, M., & Karakiulakis, G. (2012). Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermato-endocrinology.
- Jegasothy, S. M., Zabolotniaia, V., & Bielfeldt, S. (2014). Efficacy of a new topical nano-hyaluronic acid in humans. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
- Wollina, U., & Abdel-Naser, M. B. (2019). Hyaluronic acid in the treatment and prevention of skin diseases: Molecular biological, pharmaceutical and clinical aspects. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology.
Retinoic acid analogue
Retinoic acid, often referred to as tretinoin in its pharmaceutical form, is the active form of Vitamin A. It is widely recognized for its powerful effects in dermatology and skin care, particularly in treating acne and signs of skin aging.
Retinoic acid works at the cellular level to modify gene expression and affect cell growth. In treating acne, it promotes the turnover of skin cells, reducing the likelihood of pore-clogging and helping to clear existing breakouts. Additionally, it decreases the cohesiveness of follicular epithelial cells, further preventing the formation of comedones.
Retinoic acid's ability to stimulate collagen production is a key benefit in anti-aging skincare. This leads to a reduction in fine lines and wrinkles and an improvement in overall skin texture and tone. It also aids skin discoloration and hyperpigmentation by accelerating cell turnover, bringing new skin cells to the surface faster, and shedding pigmented and damaged cells.
Despite its benefits, retinoic acid can irritate the skin, causing side effects like redness, dryness, and peeling, especially during the initial period of use. Its potency means it is generally available by prescription and requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional.
Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) is a newer, esterified form of retinoic acid. Unlike cosmetic retinol, HPR binds directly to the retinoid receptors of the skin cells without needing conversion. This direct binding allows it to deliver similar benefits to retinoic acid, such as stimulating collagen production, improving skin elasticity, and reducing signs of aging, but with a lower risk of irritation.
HPR is considered more gentle and less irritating than traditional retinoic acid while offering comparable benefits. With HPR, everyone has access to the benefits of prescription retinoids without the risk of side effects.
Physiological Effects
- Cell Turnover and Renewal: HPR promotes rapid cell turnover, aiding in the exfoliation of dead skin cells and generating new cells.
- Skin Texture: Promoting cell renewal improves skin texture and addresses issues like roughness and dullness.
- Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improving skin elasticity.
- Acne Treatment: Effective in treating acne by unclogging pores and reducing the size of sebaceous glands, it diminishes both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions.
- Pigmentation: It can reduce hyperpigmentation by accelerating the turnover of hyperpigmented skin cells and inhibiting melanin production.
- Photoaging: Effective in treating signs of photoaging, reversing some of the damage caused by UV radiation.
Special Benefits
- Retinoid Receptor Activity: HPR, an ester of retinoic acid, binds directly to retinoid receptors in the skin, enabling it to work without needing to be converted into retinoic acid.
- Lower Irritation: Typically, it causes less irritation than retinoic acid, making it more suitable for sensitive skin types.
- Collagen Stimulation and Anti-Aging: Like retinoic acid, HPR helps in stimulating collagen production and has anti-aging properties.
- Acne and Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats acne and reduces hyperpigmentation, often with fewer side effects than retinoic acid.
- Stability and Penetration: HPR is more stable and lipid-soluble, so it penetrates the skin more effectively and is less prone to degradation.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., ... & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Fisher, G. J., Wang, Z. Q., Datta, S. C., Varani, J., Kang, S., & Voorhees, J. J. (1996). Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light. New England Journal of Medicine, 337(20), 1419-1428.
- Truchuelo, M. T., Jiménez, N., Jaén, P. (2018). Assessment of the efficacy of a new complex-based retinoic acid and retinol in a 3-month study using objective methods and skin biomarker analysis. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 17(3), 347-354.
- Mukherjee, S., et al. (2006). Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety. Clinical Interventions in Aging.
- Randhawa, M., et al. (2015). Hydroxypinacolone retinoate: a new retinoid and its use in dermatology. Skin Therapy Letter.
Vitamin C
Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps neutralize skin free radicals. These free radicals are generated by environmental stressors like UV radiation and pollution, which contribute to premature aging. By neutralizing these harmful molecules, vitamin C helps prevent oxidative skin damage, thereby reducing signs of aging, such as fine lines and wrinkles.
Another significant benefit of vitamin C is its role in collagen production. Collagen is a key protein that gives the skin its structure and firmness. As an essential cofactor for collagen biosynthesis, vitamin C helps maintain skin elasticity and can aid in wound healing and scar reduction.
Vitamin C is also known for its skin-brightening properties. It helps to inhibit the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin production. By reducing melanin formation, vitamin C can help lighten hyperpigmentation and even skin tone, leading to a brighter and more radiant complexion.
Tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate is a stable, oil-soluble form of vitamin C. Unlike ascorbic acid, which is water-soluble and can be unstable in certain formulations, tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate is more stable. Due to its lipid-soluble nature, it can penetrate the skin more effectively, reaching the deeper layers of the skin, stimulating collagen production, and providing antioxidant protection.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Properties: Powerful antioxidant that neutralizes free radicals caused by UV radiation and pollution, preventing oxidative stress and damage to the skin.
- Collagen Synthesis: It plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis, aiding in maintaining skin firmness and elasticity and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Brightening: Effective in reducing hyperpigmentation and evening out skin tone by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is responsible for melanin production.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it provides photoprotection by neutralizing free radicals induced by UV exposure.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Reduce signs of aging and improve skin texture.
- Hyperpigmentation: Effective in treating hyperpigmentation, sun spots, and melasma.
- Sun Damage: Help mitigate the effects of sun damage and provide some level of photoprotection.
- General Skin Health: Both forms can improve overall skin health by boosting collagen production and providing antioxidant protection.
THD Specific benefits
- Stable form of Vitamin C: Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate is a more stable, lipid-soluble vitamin C, allowing for better skin penetration and less irritation than other forms.
- Enhanced Collagen Production: It has been shown to stimulate collagen production more effectively than ascorbic acid, aiding in anti-aging and skin rejuvenation.
- Hydration and Barrier Function: Due to its lipid-soluble nature, it enhances skin hydration and reinforces the skin barrier.
References
- Pullar, J. M., et al. (2017). The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients.
- Murray, J. C., et al. (2008). A Topical Antioxidant Solution Containing Vitamins C and E Stabilized by Ferulic Acid Provides Protection for Human Skin Against Damage Caused by Ultraviolet Irradiation. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
- Al-Niaimi, F., & Chiang, N. Y. Z. (2017). Topical Vitamin C and the Skin: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
Alpha Arbutin
Alpha Arbutin is a derivative of hydroquinone and a biosynthetic active ingredient. Its primary action is inhibiting tyrosinase, a key enzyme involved in the synthesis of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Alpha Arbutin effectively reduces melanin production in the skin by inhibiting tyrosin activity. This gradually lightens hyperpigmented areas, such as age spots, melasma, and scars, resulting in a more even skin tone.
One of the significant advantages of Alpha Arbutin over other skin-lightening agents is its safety profile. Unlike hydroquinone, which has been associated with potential side effects and is restricted in many countries, Alpha Arbutin is considered safe and less irritating to the skin, even at higher concentrations. This makes it a suitable ingredient for all skin types, including sensitive skin.
In addition to its skin-lightening properties, Alpha Arbutin has also shown antioxidant effects, helping to protect the skin from oxidative stress caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
Physiological Effects
- Melanin Inhibition: Alpha Arbutin works by inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production in the skin. This action reduces the formation of melanin, leading to a lightening of skin pigmentation.
- Even Skin Tone: Regular use of alpha arbutin can lead to a more even skin tone overall, reducing the appearance of age spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Reduced Skin Discoloration: It effectively reduces the appearance of dark spots and areas of hyperpigmentation, such as those caused by acne, sun damage, or hormonal changes.
- Safer Alternative to Hydroquinone: While structurally similar to hydroquinone, alpha arbutin is a safer option with a lower risk of side effects.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Hyperpigmentation: Alpha arbutin treats melasma, sun spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne.
- Skin Brightening: Provide a more radiant and uniform skin tone.
- Anti-Aging: Reduce the appearance of age-related spots and uneven skin tone.
Sunscreen
Using sunscreen is a fundamental aspect of skin care and preventive dermatology. It's essential for reducing the risk of skin cancers and photoaging and maintaining overall skin health in the face of constant exposure to UV radiation.
Sunscreen is a vital skincare product designed to protect the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Two primary types of UV radiation affect the skin: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and are primarily responsible for aging and long-term skin damage, whereas UVB rays cause sunburn and play a key role in developing skin cancer.
Sunscreen products work by either absorbing, reflecting, or scattering sunlight. They contain chemical compounds that absorb UV radiation and convert it into a small amount of heat or physical compounds (like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) that act as a physical barrier, reflecting UV light away from the skin.
The effectiveness of sunscreen is measured by its Sun Protection Factor (SPF). SPF indicates how well the sunscreen protects against UVB rays. For example, an SPF of 30 means it would take 30 times longer for your skin to burn than without sunscreen. However, it's important to note that no sunscreen can block 100% UV rays.
Regular use of sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 can reduce the risk of skin cancer, prevent sunburn, and slow down the skin's aging process.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Prevention of Sunburn: Sunscreen protects the skin from UVB rays, which cause sunburn. This reduces the immediate risk of skin damage and discomfort.
- Skin Cancer Prevention: Regular use of sunscreen significantly lowers the risk of developing various types of skin cancer, especially melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma.
- Prevention of Photoaging: Sunscreen also shields the skin from UVA rays, which penetrate deeper into the skin and are primarily responsible for photoaging, including wrinkles, leathery skin, and sunspots.
- Protection Against Photosensitivity: Sunscreen helps prevent flare-ups triggered by sun exposure for individuals with photosensitive skin conditions like lupus or rosacea.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: It aids in preventing and managing hyperpigmentation and melasma, conditions exacerbated by sun exposure.
- General Skin Health: Sunscreen helps maintain overall skin health and integrity by protecting the skin from UV damage.
References
- Burnett, M. E., & Wang, S. Q. (2011). Current sunscreen controversies: a critical review. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine.
- Green, A. C., et al. (2011). Reduced melanoma after regular sunscreen use: randomized trial follow-up. Journal of Clinical Oncology.
- Hughes, M. C. B., et al. (2013). Sunscreen and Prevention of Skin Aging: A Randomized Trial. Annals of Internal Medicine.
Azelaic acid
Azelaic acid, a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid, is an effective ingredient in dermatological treatments, particularly for acne, rosacea, and hyperpigmentation, with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Physiological Effects
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Azelaic acid reduces inflammation, effectively treating inflammatory skin conditions like acne and rosacea.
- Antimicrobial Action: It possesses antimicrobial properties that target acne-causing bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes), helping to reduce acne outbreaks.
- Keratolytic Effects: It helps unclog pores and reduce the formation of comedones (black and whiteheads) by normalizing the shedding of skin cells.
- Depigmenting Agent: Azelaic acid effectively treats hyperpigmentation disorders, including melasma, as it inhibits tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin production.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne: Azelaic acid inhibits the proliferation of acne-causing bacteria on the skin’s surface, thereby reducing bacterial growth and inflammation. Its antibacterial activity is primarily against Propionibacterium acnes, a key bacterium involved in the development of acne. Furthermore, azelaic acid helps unclog pores and reduce skin cell buildup, effectively treating mild to moderate acne.
- Rosacea: Azelaic acid's anti-inflammatory action helps to reduce redness and swelling associated with rosacea. In addition, azelaic acid's ability to reduce keratinization (the process by which skin cells become more fibrous and less flexible) contributes to its effectiveness in this condition.
- Pigmentation: Azelaic acid effectively treats melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme in melanin production. This helps to reduce the formation of excess pigment and can lead to a more even skin tone.
References
- Fitton, A., & Goa, K. L. (1991). Azelaic Acid. Drugs.
- Gollnick, H., & Schramm, M. (1998). Topical drug treatment in acne. Dermatology.
- Passeron, T., et al. (2019). Melasma treatment: A novel approach using a topical agent that contains an anti-estrogen and a low-dose retinoid. G Ital Dermatol Venereol.
- Wolf, J. E., Kerrouche, N., & Arsonnaud, S. (2006). Efficacy and safety of once-daily metronidazole 1% gel compared with twice-daily azelaic acid 15% gel in the treatment of rosacea. Cutis, 77(4 Suppl), 3-11.
- Hollinger, J. C., Angra, K., & Halder, R. M. (2018). Are natural ingredients effective in the management of hyperpigmentation? A systematic review. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology, 11(2), 28.
MORNING
EVENING
MORNING
EVENING
Morning Regimen Notes
For the best use of Renewal Facial Cleanser, please refer to the detailed instructions on its product page. You can access this page by clicking on the cleanser's name above.
Apply Collagen Serum to damp skin every morning after cleansing.
Apply Dermdefence SPF 50 a few minutes after you apply your serum.
- After you apply Collagen Serum, wait a few minutes, then layer with Litaderm Serum.
- After you apply Litaderm Serum, wait a few minutes, then layer with Dermdefence SPF 50.
- You should not follow the intensified treatment regimen if you have very sensitive skin.
Evening Regimen Notes
For the best use of Renewal Facial Cleanser, please refer to the detailed instructions on its product page. You can access this page by clicking on the cleanser's name above.
Apply Retinol Serum on damp skin in the evening after cleansing.
After you apply your Retinol Serum, wait a few minutes then layer with Litaderm Serum.
If you have sensitive skin, use Litaderm Serum only 2-3 times per week.
- Start using the Glycolic Gel once a week after cleansing instead of your serum.
- If your skin adjusts well, you can increase the frequency to 2-3 times a week as your skin becomes more tolerant.
When applying Glycolic Gel, don't layer it with another product in the evenings. Other products can make Glycolic Gel less effective by changing its pH.
Important Notes
- Reduce the use of Glycolic Gel to one evening a week or even one evening every two weeks.
- When irritation subsides, slowly increase the frequency of Glycolic Gel application to 2-3 times per week, as your skin tolerates it.
- If irritation symptoms continue, reduce the frequency of Litaderm Serum application to once or twice weekly.
- When irritation subsides, slowly increase the frequency of Litaderm Serum application again as your skin tolerates it.
- You should not follow the Intensify treatment guidelines if you have sensitive skin.
(Based on your selection)
(Based on your selection)
Aging Skin with Pigmentation
your treatment pack
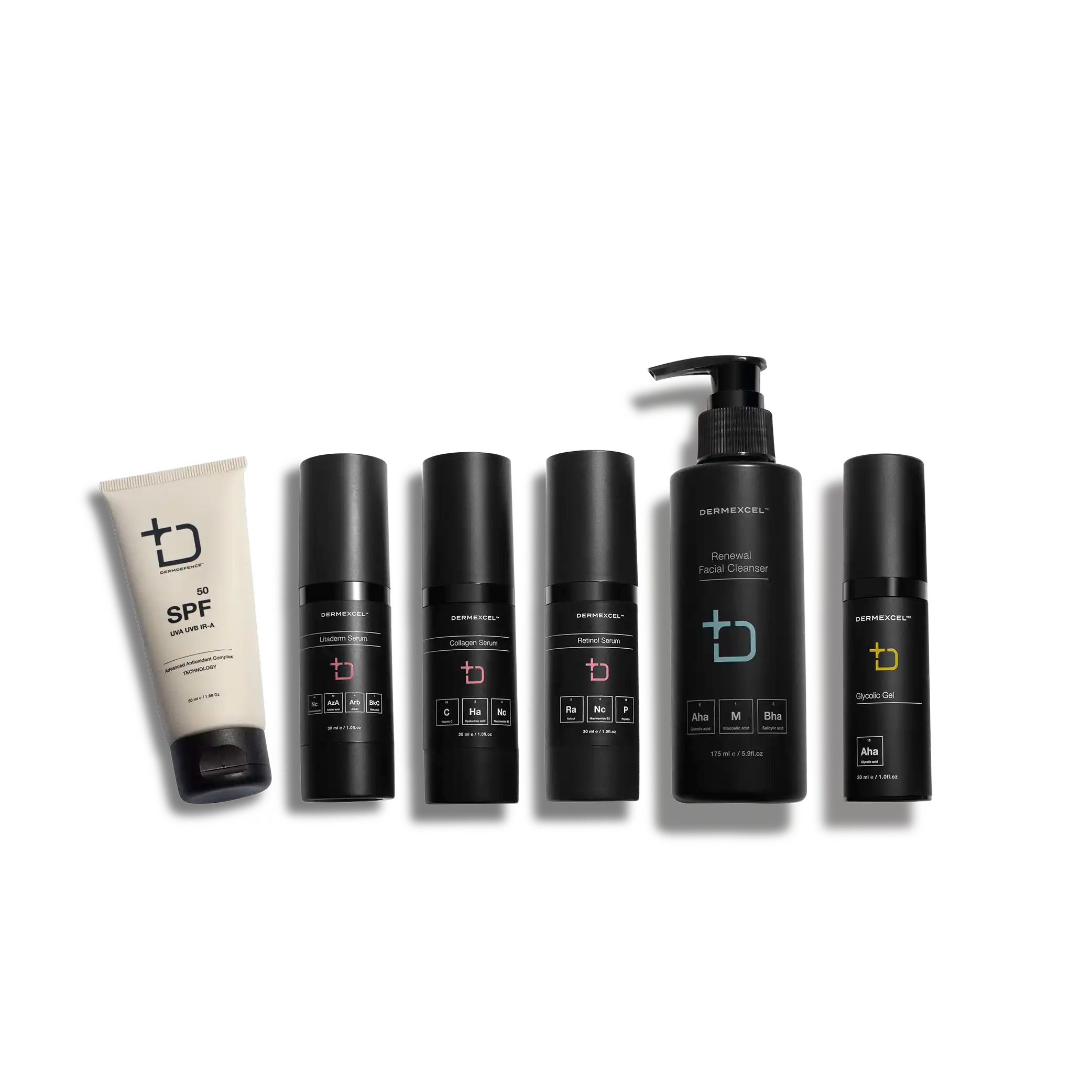
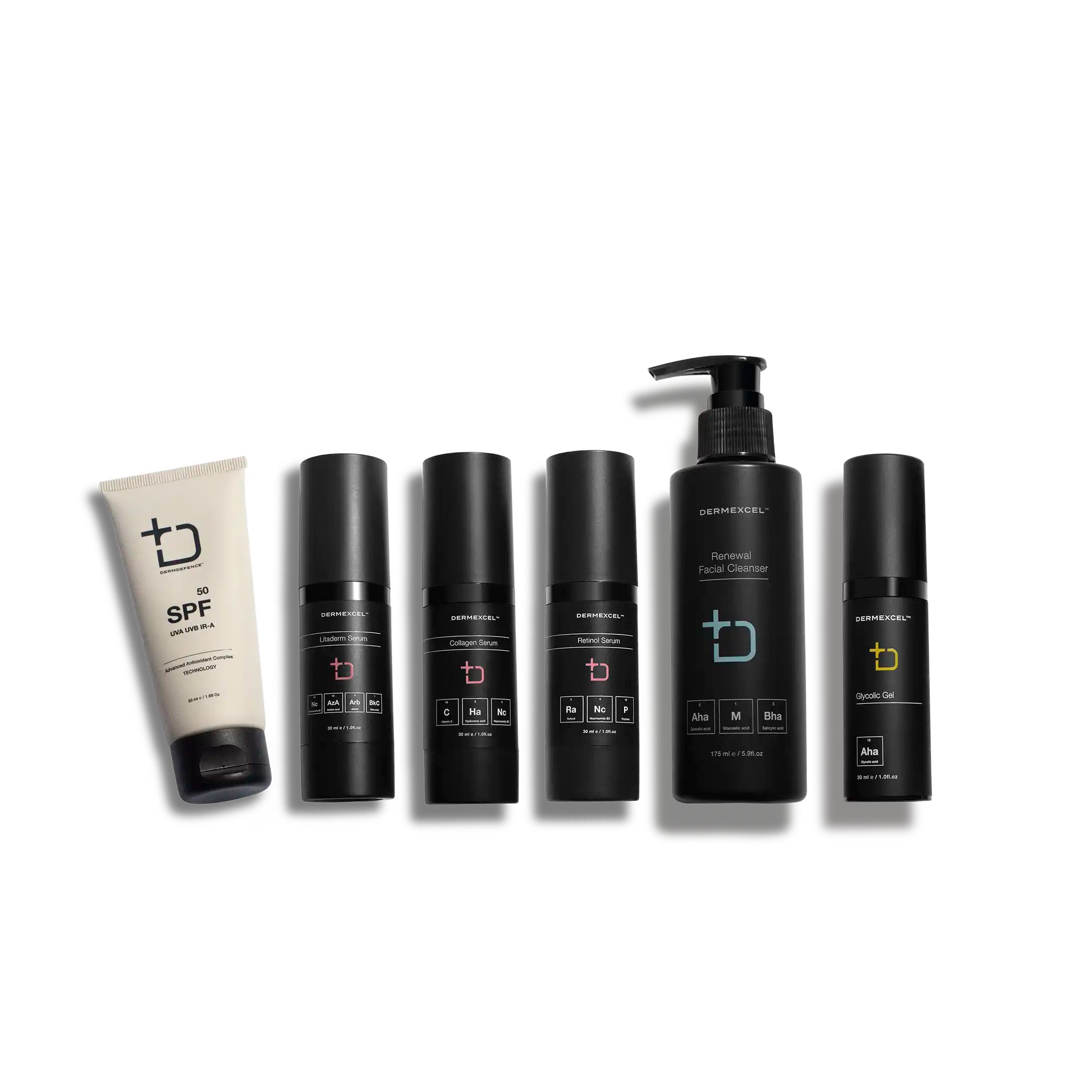
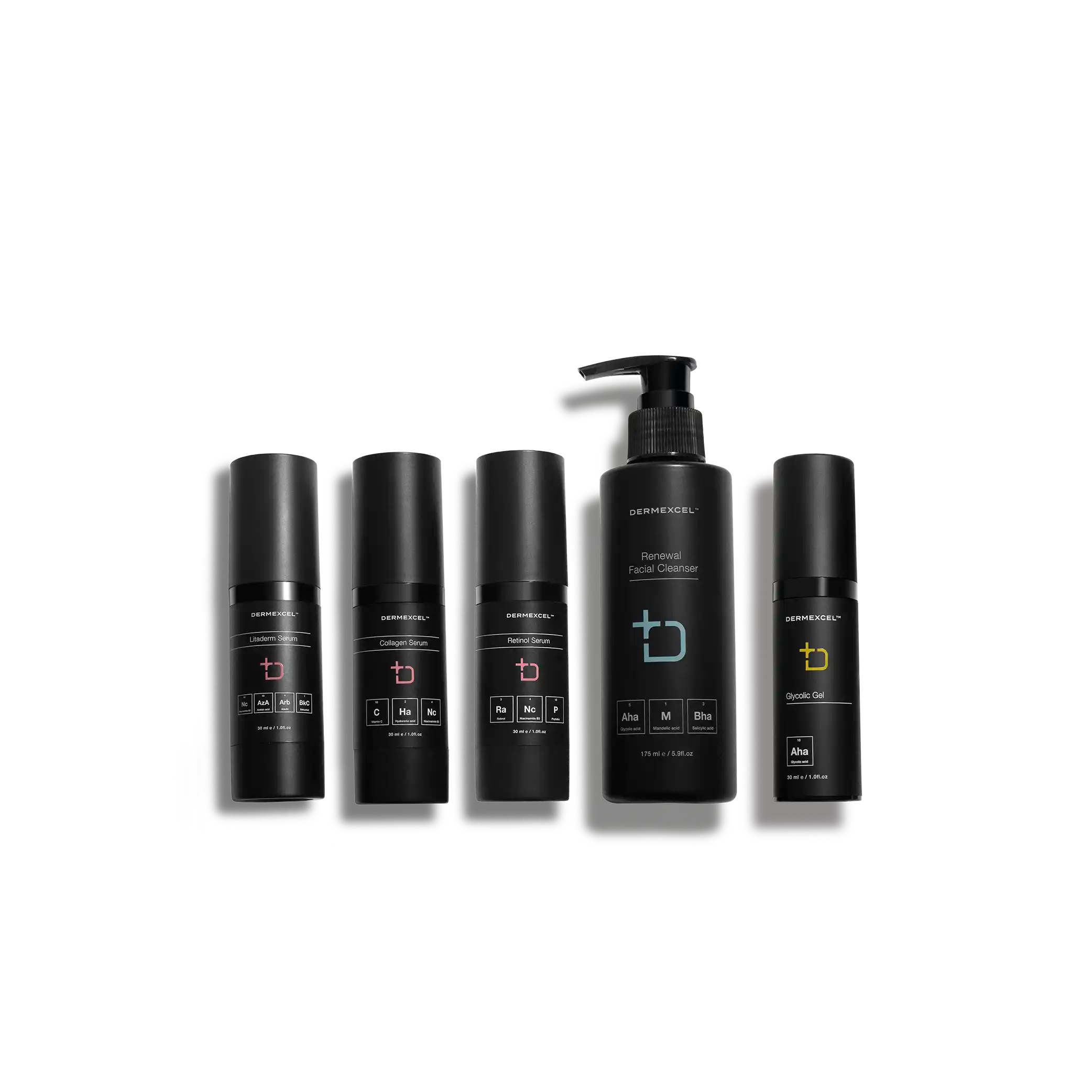








Treatment pack for Aging.Pigmentation

DNA repair

Skin Smoothing

↑ Elasticity

↓ pigmentation

Anti-Aging

Choose options
Aging Skin with Pigmentation
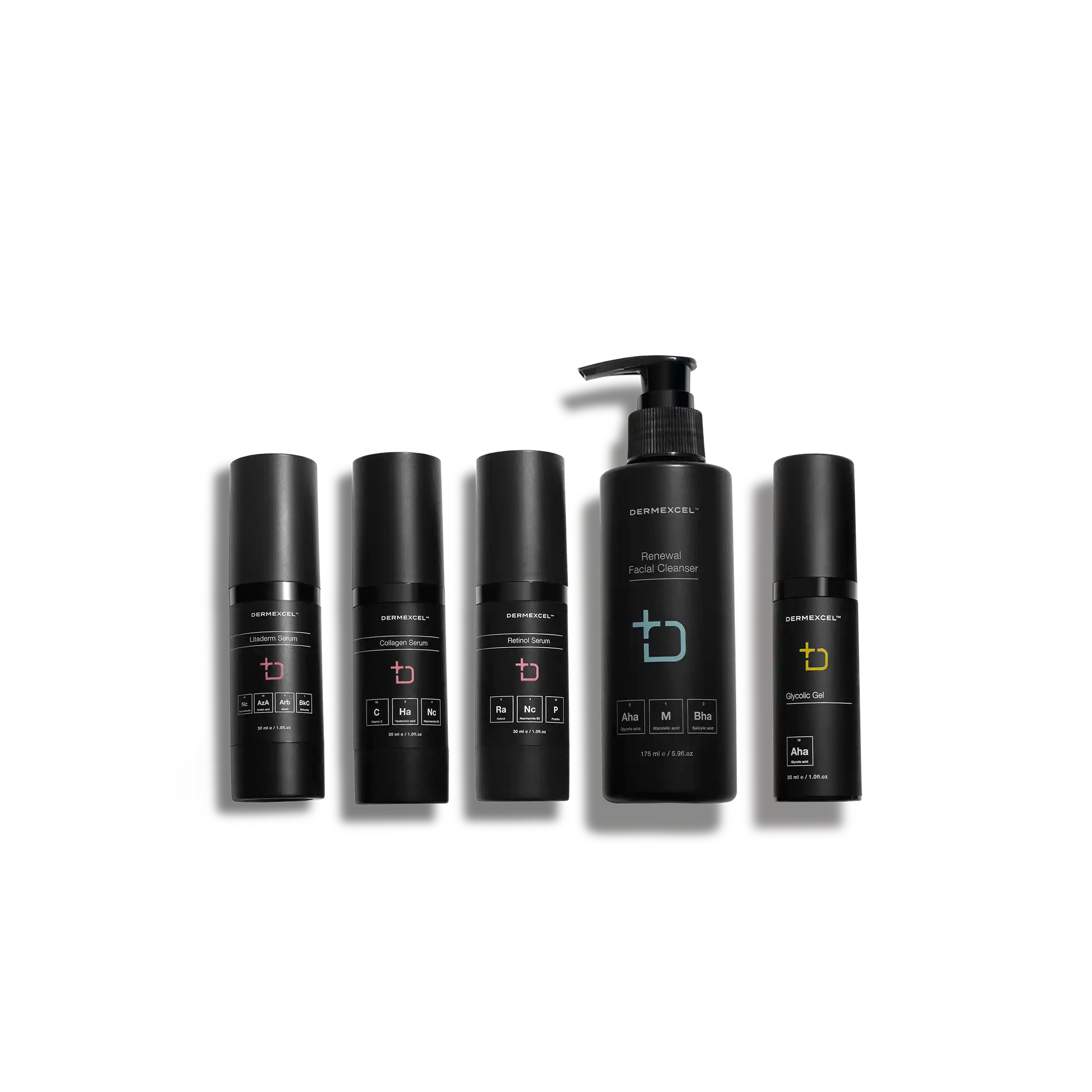
products in your treatment pack








Unclog Pores

Minimize Pores

anti-aging

smooth skin

Brightening
Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is highly acclaimed for its remarkable exfoliating and rejuvenating properties. Its small molecular size enables deep skin penetration, fostering efficient exfoliation at the cellular level.
Glycolic acid’s water solubility allows it to penetrate the upper layers of the skin easily. Its primary mechanism of action involves weakening the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their shedding, and revealing the newer, healthier skin beneath. This process of accelerated cell turnover is instrumental in addressing a range of skin concerns, from aging signs like fine lines and wrinkles to texture irregularities and hyperpigmentation.
Glycolic acid's efficacy extends beyond mere exfoliation. It's also recognized for stimulating collagen production, a crucial protein in maintaining skin's elasticity and firmness. This aspect contributes to its anti-aging benefits. Furthermore, its hydrating properties add to its appeal, as they help increase the skin's capacity to retain moisture, leading to a more supple and vibrant complexion.
Clinical studies have consistently supported glycolic acid's role in improving skin appearance. Research indicates significant improvements in skin texture and pigmentation and the visible reduction of wrinkles and fine lines with glycolic acid.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: Glycolic acid is a powerful exfoliant. It dissolves the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, facilitating their removal and revealing newer, healthier skin underneath.
- Increased Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, essential for skin elasticity and firmness. This action helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Enhanced Skin Hydration: Glycolic acid improves the skin's ability to retain moisture, enhancing hydration and a more plump, vibrant skin appearance.
- Skin Brightening: Removing dead skin cells can brighten the complexion and reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Improved Skin Texture: Regular use of glycolic acid can lead to smoother, more even textured skin, making it beneficial for conditions like keratosis pilaris.
- Acne Treatment: Its exfoliating properties help in unclogging pores, thereby reducing the occurrence of acne breakouts.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Glycolic acid is widely used in anti-aging products to reduce signs of aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: It helps manage acne by exfoliating the skin and removing blockage from pores.
- Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats hyperpigmentation by accelerating the removal of hyperpigmented skin cells.
- Textural Irregularities: Glycolic acid improves skin texture, treating keratosis pilaris and other rough skin conditions.
- Sun-Damaged Skin: It helps rejuvenate sun-damaged skin by accelerating cell turnover and collagen synthesis.
References
- Bernstein, E. F. (2001). Glycolic acid treatment increases type I collagen mRNA and hyaluronic acid content of human skin. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Sharad, J. (2013). Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 35(3), 388-391.
Mandelic acid
Despite its gentler nature, mandelic acid potently accelerates cell turnover, removes dead skin cells, and promotes a fresher, more rejuvenated skin appearance.
Mandelic acid's efficacy extends to a wide range of skin concerns. It's particularly beneficial in treating acne, as its antibacterial properties are effective against various strains of bacteria commonly associated with acne development. Moreover, it's known for regulating sebum production and reducing inflammation, further contributing to its acne-fighting capabilities.
Additionally, mandelic acid has shown promise in addressing hyperpigmentation. Its ability to inhibit melanin production helps reduce age spots, sun spots, and uneven skin tones, making it a valuable ingredient in skincare products targeting pigmentation issues. Studies have documented its effectiveness in improving skin texture and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, offering a multifaceted approach to skin rejuvenation.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: Mandelic acid gently exfoliates the skin by loosening the bonds between dead skin cells on the surface, promoting their removal and revealing fresh, new skin underneath.
- Antibacterial Properties: It possesses antibacterial properties, making it effective against acne-causing bacteria.
- Reducing Hyperpigmentation: Mandelic acid is known for its ability to reduce hyperpigmentation, including age spots, sun spots, and marks left by acne, due to its ability to inhibit melanin production.
- Anti-aging Effects: It stimulates collagen production, which can help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improve the overall texture of aging skin.
- Suitability for Sensitive Skin: Due to its larger molecular size than other AHAs, mandelic acid penetrates the skin more slowly and is less likely to irritate, making it suitable for sensitive skin types.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne Treatment: Its exfoliating and antibacterial properties make mandelic acid effective in treating acne, particularly in those with sensitive skin.
- Melasma and Hyperpigmentation: It is beneficial in treating melasma and other forms of hyperpigmentation, lightening dark spots without causing significant irritation.
- Aging Skin: Mandelic acid is used in anti-aging skin care products to improve skin texture and diminish signs of aging.
- Photo-Aging: It can help to reverse some of the damage caused by UV radiation, such as fine lines and uneven skin tone.
References
- Briden, M. E. (2004). Noninvasive treatments of acne. In Acne and its Therapy (pp. 341-357). Marcel Dekker.
- Taylor, M. B. (1999). Summary of mandelic acid for the improvement of skin conditions. Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Sharad, J. (2013). Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid, a renowned beta hydroxy acid (BHA), is a cornerstone in dermatology and skincare due to its exceptional keratolytic and comedolytic properties. Its unique ability to penetrate oil-laden hair follicle pores makes it particularly effective in treating acne-prone and oily skin types.
Salicylic acid dissolves skin debris (sebum and dead skin cells) that clogs pores and causes acne. It's a mild antibacterial and powerful anti-inflammatory agent that helps reduce the redness and swelling associated with breakouts.
What sets salicylic acid apart in dermatological treatments is its ability to exfoliate the skin, not just on the surface but within the pores themselves. This is due to its oil-soluble nature, which allows it to penetrate deep into the pores and dissolve the keratin plugs that lead to blackheads and whiteheads.
Furthermore, salicylic acid also has the capacity to adjust the pH of the skin, creating an environment less favorable for the growth of acne-causing bacteria. Salicylic acid's efficacy in treating various skin conditions, particularly acne, has been extensively documented in the scientific literature. Studies have consistently shown its ability to reduce acne lesions in terms of count and severity. Additionally, salicylic acid is highly recommended for its effectiveness in treating other skin conditions, such as psoriasis and dandruff, due to its ability to soften and remove scales and flakes from the skin.
Physiological Effects
- Keratolytic Action: Salicylic acid is known for its ability to exfoliate the skin by dissolving the intercellular 'glue' that holds skin cells together, helping to remove dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- Comedolytic Effect: It is particularly effective in reducing comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) by unclogging pores and preventing the formation of new comedones.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Salicylic acid reduces inflammation, which is beneficial in treating acne and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps to regulate oil production, making it a valuable ingredient for managing oily and acne-prone skin.
- Penetration Enhancement: Due to its lipophilic nature, it can penetrate sebum-filled follicles, effectively treating acne located deep within the pores.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne Vulgaris: Salicylic acid is a cornerstone in acne treatment, effectively preventing and treating existing acne lesions.
- Psoriasis: Its keratolytic properties make it helpful in softening and removing scales associated with psoriasis.
- Warts: Salicylic acid is commonly used to treat warts because it can exfoliate and remove thick skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: It helps manage seborrheic dermatitis by reducing scaling and redness.
- Keratosis Pilaris: Salicylic acid can aid in smoothing the rough bumps associated with peratosis Pilaris.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 3, 135.
- Zander, E., & Weisman, S. (1992). Treatment of acne vulgaris with salicylic acid pads. Clinical Therapeutics.
- Gupta, A. K., & Nicol, K. (2004). The use of sulfur in dermatology. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.






SIZE: 30 mL

Antioxidant

Even Skin Tone

↑ Collagen

anti-aging

Moisturizing
Vitamin C
Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps neutralize skin free radicals. These free radicals are generated by environmental stressors like UV radiation and pollution, which contribute to premature aging. By neutralizing these harmful molecules, vitamin C helps prevent oxidative skin damage, thereby reducing signs of aging, such as fine lines and wrinkles.
Another significant benefit of vitamin C is its role in collagen production. Collagen is a key protein that gives the skin its structure and firmness. As an essential cofactor for collagen biosynthesis, vitamin C helps maintain skin elasticity and can aid in wound healing and scar reduction.
Vitamin C is also known for its skin-brightening properties. It helps to inhibit the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin production. By reducing melanin formation, vitamin C can help lighten hyperpigmentation and even skin tone, leading to a brighter and more radiant complexion.
Tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate is a stable, oil-soluble form of vitamin C. Unlike ascorbic acid, which is water-soluble and can be unstable in certain formulations, tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate is more stable. Due to its lipid-soluble nature, it can penetrate the skin more effectively, reaching the deeper layers of the skin, stimulating collagen production, and providing antioxidant protection.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Properties: Powerful antioxidant that neutralizes free radicals caused by UV radiation and pollution, preventing oxidative stress and damage to the skin.
- Collagen Synthesis: It plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis, aiding in maintaining skin firmness and elasticity and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Brightening: Effective in reducing hyperpigmentation and evening out skin tone by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is responsible for melanin production.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it provides photoprotection by neutralizing free radicals induced by UV exposure.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Reduce signs of aging and improve skin texture.
- Hyperpigmentation: Effective in treating hyperpigmentation, sun spots, and melasma.
- Sun Damage: Help mitigate the effects of sun damage and provide some level of photoprotection.
- General Skin Health: Both forms can improve overall skin health by boosting collagen production and providing antioxidant protection.
THD Specific benefits
- Stable form of Vitamin C: Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate is a more stable, lipid-soluble vitamin C, allowing for better skin penetration and less irritation than other forms.
- Enhanced Collagen Production: It has been shown to stimulate collagen production more effectively than ascorbic acid, aiding in anti-aging and skin rejuvenation.
- Hydration and Barrier Function: Due to its lipid-soluble nature, it enhances skin hydration and reinforces the skin barrier.
References
- Pullar, J. M., et al. (2017). The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients.
- Murray, J. C., et al. (2008). A Topical Antioxidant Solution Containing Vitamins C and E Stabilized by Ferulic Acid Provides Protection for Human Skin Against Damage Caused by Ultraviolet Irradiation. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
- Al-Niaimi, F., & Chiang, N. Y. Z. (2017). Topical Vitamin C and the Skin: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan found throughout the body's connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. Most abundantly present in the skin, eyes, and synovial fluid, HA is renowned for its exceptional capacity to retain moisture — a single gram can hold up to six liters of water.
In skincare, the primary appeal of hyaluronic acid lies in its unparalleled hydrating abilities. As a humectant, HA attracts and retains moisture from the environment, providing intense hydration to the skin. This hydrating property contributes significantly to maintaining skin plumpness, suppleness, and elasticity.
Beyond hydration, hyaluronic acid also plays a vital role in skin repair and regeneration. It supports the skin's healing and repair processes, and its anti-inflammatory properties help calm irritated skin. Moreover, HA's ability to promote collagen production, a crucial protein for skin elasticity, further underscores its anti-aging benefits.
The molecular size of hyaluronic acid influences its skin penetration and efficacy. High-molecular-weight HA remains on the skin's surface, providing hydration and forming a barrier against moisture loss. In contrast, low-molecular-weight HA penetrates deeper into the skin's layers, offering more profound hydrating and rejuvenating effects.
Hyaluronic acid's remarkable ability to hydrate, improve skin elasticity, aid in wound healing, and provide antioxidant protection makes it valuable in managing various dermatological conditions, particularly aging, dryness, and sensitive skin.
Physiological Effects
- Hydration: Hyaluronic acid is a powerful humectant that can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water, significantly enhancing skin hydration and leading to plumper, more hydrated skin.
- Skin Elasticity and Wrinkle Reduction: By increasing skin moisture, it improves skin elasticity, reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and gives the skin a more youthful appearance.
- Wound Healing: It plays a role in wound healing due to its ability to regulate inflammation levels and signal the body to build more blood vessels in the damaged area.
- Barrier Enhancement: Hyaluronic acid helps reinforce the skin's natural barriers, protecting against environmental factors and retaining moisture.
- Antioxidant Properties: It provides antioxidant defense against free-radical damage from the sun and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Its ability to reduce wrinkles and improve skin elasticity makes it popular in anti-aging skincare products.
- Dry Skin: Hyaluronic acid is beneficial in treating dry skin conditions by providing intense hydration.
- Wound Care: Its role in wound healing is leveraged in post-procedure care, such as after laser treatments, and in healing minor cuts and abrasions.
- Acne Scars: It can help treat acne scars by promoting skin regeneration and reducing inflammation.
- Sensitive Skin: Hyaluronic acid is suitable for sensitive skin due to its gentle nature. It provides hydration without irritating.
References
- Papakonstantinou, E., Roth, M., & Karakiulakis, G. (2012). Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermato-endocrinology.
- Jegasothy, S. M., Zabolotniaia, V., & Bielfeldt, S. (2014). Efficacy of a new topical nano-hyaluronic acid in humans. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
- Wollina, U., & Abdel-Naser, M. B. (2019). Hyaluronic acid in the treatment and prevention of skin diseases: Molecular biological, pharmaceutical and clinical aspects. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
Hydrotensyl Complex
An active ingredient made from the combination of 3 powerful actives with extraordinary benefits for the skin:
- Honey Extract
- Marine native Collagen
- Marine Hydrolyzed Elastin
Honey Extract
- Provides natural moisturising factor analogue substances to skin cells.
- It also provides the skin with components with a vital capacity for hydro-retention and hydro-regulation.
- Mechanisms of action on skin cells include antioxidant activity and the induction of cytokines, and matrix metalloproteinase expression.
Marine native Collagen
Native Collagen has a high molecular weight, that leaves a protective film on the skin with tensor effects and remarkable moisturizing capabilities.
Marine Hydrolyzed Elastin
- Provide nutrients and amino acids that the fibroblasts (type of skin cell) will use to produce new fibres of elastin and collagen.
- It contains the peptides and amino acids of elastin: Aspartic Acid, Theorine, Serine, Glutamic Acid, Proline, Glycine, Lysine, and Arginine.
It is a complete active ingredient from which the skin will get substances to nourish, increase its moisture, get external protection against damaging substances, and decrease its wrinkles.






SIZE: 30 mL

Unclog Pores

Minimize Pores

Smooth Skin

anti-aging

DNA repair
Retinoic acid analogue
Retinoic acid, often referred to as tretinoin in its pharmaceutical form, is the active form of Vitamin A. It is widely recognized for its powerful effects in dermatology and skin care, particularly in treating acne and signs of skin aging.
Retinoic acid works at the cellular level to modify gene expression and affect cell growth. In treating acne, it promotes the turnover of skin cells, reducing the likelihood of pore-clogging and helping to clear existing breakouts. Additionally, it decreases the cohesiveness of follicular epithelial cells, further preventing the formation of comedones.
Retinoic acid's ability to stimulate collagen production is a key benefit in anti-aging skincare. This leads to a reduction in fine lines and wrinkles and an improvement in overall skin texture and tone. It also aids skin discoloration and hyperpigmentation by accelerating cell turnover, bringing new skin cells to the surface faster, and shedding pigmented and damaged cells.
Despite its benefits, retinoic acid can irritate the skin, causing side effects like redness, dryness, and peeling, especially during the initial period of use. Its potency means it is generally available by prescription and requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional.
Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) is a newer, esterified form of retinoic acid. Unlike cosmetic retinol, HPR binds directly to the retinoid receptors of the skin cells without needing conversion. This direct binding allows it to deliver similar benefits to retinoic acid, such as stimulating collagen production, improving skin elasticity, and reducing signs of aging, but with a lower risk of irritation.
HPR is considered more gentle and less irritating than traditional retinoic acid while offering comparable benefits. With HPR, everyone has access to the benefits of prescription retinoids without the risk of side effects.
Physiological Effects
- Cell Turnover and Renewal: HPR promotes rapid cell turnover, aiding in the exfoliation of dead skin cells and generating new cells.
- Skin Texture: Promoting cell renewal improves skin texture and addresses issues like roughness and dullness.
- Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improving skin elasticity.
- Acne Treatment: Effective in treating acne by unclogging pores and reducing the size of sebaceous glands, it diminishes both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions.
- Pigmentation: It can reduce hyperpigmentation by accelerating the turnover of hyperpigmented skin cells and inhibiting melanin production.
- Photoaging: Effective in treating signs of photoaging, reversing some of the damage caused by UV radiation.
Special Benefits
- Retinoid Receptor Activity: HPR, an ester of retinoic acid, binds directly to retinoid receptors in the skin, enabling it to work without needing to be converted into retinoic acid.
- Lower Irritation: Typically, it causes less irritation than retinoic acid, making it more suitable for sensitive skin types.
- Collagen Stimulation and Anti-Aging: Like retinoic acid, HPR helps in stimulating collagen production and has anti-aging properties.
- Acne and Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats acne and reduces hyperpigmentation, often with fewer side effects than retinoic acid.
- Stability and Penetration: HPR is more stable and lipid-soluble, so it penetrates the skin more effectively and is less prone to degradation.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., ... & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Fisher, G. J., Wang, Z. Q., Datta, S. C., Varani, J., Kang, S., & Voorhees, J. J. (1996). Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light. New England Journal of Medicine, 337(20), 1419-1428.
- Truchuelo, M. T., Jiménez, N., Jaén, P. (2018). Assessment of the efficacy of a new complex-based retinoic acid and retinol in a 3-month study using objective methods and skin biomarker analysis. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 17(3), 347-354.
- Mukherjee, S., et al. (2006). Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety. Clinical Interventions in Aging.
- Randhawa, M., et al. (2015). Hydroxypinacolone retinoate: a new retinoid and its use in dermatology. Skin Therapy Letter.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
Peptides
Peptides are short chains of amino acids with a wide range of biological functions and skin benefits. They are essentially small fragments of proteins, which are fundamental components of all living cells, including collagen and elastin in the skin.
In skincare, peptides are known for enhancing skin repair and rejuvenation. They function as signaling molecules, instructing cells to perform specific tasks such as producing collagen and elastin, vital for maintaining the skin's firmness and elasticity. This makes peptides especially beneficial in anti-aging products, as they can help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Research has shown that certain peptides can improve skin barrier function, increase hydration, and soothe skin inflammation. This makes them suitable for products targeting dry, sensitive, or inflamed skin.
Peptides, with their diverse functions in promoting collagen production, strengthening the skin barrier, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory actions, are pivotal in managing various dermatological conditions, particularly in anti-aging, sensitive skin care, and wound healing applications.
Physiological Effects
- Collagen Production: Certain peptides, known as signal peptides, stimulate collagen production in the skin, enhancing skin firmness and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Barrier Strengthening: Peptides can strengthen the skin barrier, improve hydration, and protect against environmental damage.
- Wound Healing: Some peptides play a role in the skin's natural healing process, aiding tissue repair and regeneration.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Certain peptides have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to soothe and calm irritated skin.
- Antimicrobial Action: Some peptides possess antimicrobial properties, potentially helping to manage acne and other skin infections.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Peptides can stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity.
- Sensitive Skin Conditions: Peptides are beneficial for sensitive or inflamed skin due to their soothing properties.
- Acne-Prone Skin: Antimicrobial peptides can be effective in acne treatment formulations.
- Wound Care and Repair: Peptides improve wound healing and reduce scarring.
References
- Gorouhi, F., & Maibach, H. I. (2009). Role of topical peptides in preventing or treating aged skin. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Schagen, S. K. (2012). Topical peptide treatments with effective anti-aging results. Cosmetics.
- Varani, J., et al. (2001). Vitamin A antagonizes decreased cell growth and elevated collagen-degrading matrix metalloproteinases and stimulates collagen accumulation in naturally aged human skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Matrixyl 3000
Matrixyl 3000: The Powerhouse of Anti-Aging Peptides
Matrixyl 3000, a trademarked peptide composition, has revolutionized the approach towards anti-aging in dermatological products. This innovative ingredient combines two peptides, Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1 and Palmitoyl Tetrapeptide-7. The synergy of these peptides enhances skin repair and reduces the appearance of aging.
Physiological Effects
- Collagen and Elastin Stimulation: Matrixyl 3000 promotes the production of collagen and elastin, key proteins that provide skin structure and elasticity. This helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Repair and Regeneration: It aids in the skin's repair process, enhancing the overall texture and tone, and may help reverse the signs of aging.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Matrixyl 3000 can have anti-inflammatory effects, reducing inflammation and potentially aiding in skin repair.
- Hydration Enhancement: Improving the underlying skin structure can enhance hydration, leading to a plumper, more youthful appearance.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Its primary use is in anti-aging skincare products to combat wrinkles, fine lines, and other signs of aging.
- Improving Skin Texture and Tone: Matrixyl 3000 can improve overall skin texture, which is beneficial for skin that has lost smoothness or become rough due to aging.
- Skin Elasticity: It can help improve skin elasticity, making it appear firmer and more toned.
Biochemical Mechanism and Clinical Efficacy
Matrixyl 3000 mimics the appearance of broken-down collagen, causing the skin to react by producing more collagen and elastin. Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1 is known for stimulating collagen synthesis and firming the skin, while Palmitoyl Tetrapeptide-7 reduces inflammation, a key contributor to aging.
Studies have shown that Matrixyl 3000 significantly improves skin elasticity and reduces wrinkle depth. A notable study published in the "International Journal of Cosmetic Science" demonstrated that Matrixyl 3000 reduced wrinkle volume and depth by up to 45% after 2 months of use (Smith, 2005).
Matrixyl 3000 stands out as a non-irritating, highly effective ingredient. Its role in stimulating collagen and elastin production and reducing inflammation is a cornerstone in anti-aging skincare regimens.
References
- Smith, J. (2005). "Effects of Matrixyl 3000 on Skin Aging." International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Sederma Inc., "Matrixyl 3000 Technical Overview."
- Blackburn, R. S., et al. (2005). Matrixyl 3000 restores skin's metabolic balance. Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Lintner, K., et al. (2007). Matrixyl 3000: A new approach to anti-aging. Personal Care Magazine.
- Gorouhi, F., & Maibach, H. I. (2009). Role of topical peptides in preventing or treating aged skin. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8: The Innovative Peptide in Anti-Aging Dermatology
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 is a testament to the advancements in peptide technology in dermatology. Its ability to reduce facial muscle contractions non-invasively positions it as an essential ingredient in anti-aging skincare.
Biochemical Mechanism
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 functions by inhibiting the neurotransmitters that trigger muscle contractions. This action reduces the intensity of wrinkle-causing facial expressions, leading to a visible decrease in fine lines and wrinkles. It mimics the N-terminal end of SNAP-25, competing with this natural protein for a position in the SNARE complex, thereby destabilizing it. As a result, neurotransmitter release is diminished, and facial muscle contractions are softened.
Physiological Effects
- Neurotransmitter Inhibition: Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 works by inhibiting neurotransmitter release. This leads to reduced facial muscle contraction, a mechanism similar to Botox but less invasive.
- Reduction of Expression Lines: Helps to reduce the appearance of expression lines, particularly around the forehead and eyes, by limiting muscle contraction.
- Improvement in Skin Texture: Regular use can lead to smoother skin texture and a reduction in the depth and severity of wrinkles.
Special Benefits
Clinical Efficacy - Clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 in reducing wrinkle depth. A study published in the "International Journal of Cosmetic Science" reported that a cream containing 10% Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 reduced wrinkles by 30% over 30 days (Blanes-Mira et al., 2002).
References
- Blanes-Mira, C., et al. (2002). A synthetic hexapeptide (Argireline) with antiwrinkle activity. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Wang, Y., et al. (2013). The anti-wrinkle efficacy of Argireline. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy.
- Ruiz, M. A., et al. (2007). New cosmetic formulations containing Argireline. Journal of Cosmetic Science.





SIZE: 30 mL

Even Skin Tone

Moisturizing

anti-redness

anti-aging

↓ inflammation
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
Azelaic acid
Azelaic acid, a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid, is an effective ingredient in dermatological treatments, particularly for acne, rosacea, and hyperpigmentation, with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Physiological Effects
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Azelaic acid reduces inflammation, effectively treating inflammatory skin conditions like acne and rosacea.
- Antimicrobial Action: It possesses antimicrobial properties that target acne-causing bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes), helping to reduce acne outbreaks.
- Keratolytic Effects: It helps unclog pores and reduce the formation of comedones (black and whiteheads) by normalizing the shedding of skin cells.
- Depigmenting Agent: Azelaic acid effectively treats hyperpigmentation disorders, including melasma, as it inhibits tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin production.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne: Azelaic acid inhibits the proliferation of acne-causing bacteria on the skin’s surface, thereby reducing bacterial growth and inflammation. Its antibacterial activity is primarily against Propionibacterium acnes, a key bacterium involved in the development of acne. Furthermore, azelaic acid helps unclog pores and reduce skin cell buildup, effectively treating mild to moderate acne.
- Rosacea: Azelaic acid's anti-inflammatory action helps to reduce redness and swelling associated with rosacea. In addition, azelaic acid's ability to reduce keratinization (the process by which skin cells become more fibrous and less flexible) contributes to its effectiveness in this condition.
- Pigmentation: Azelaic acid effectively treats melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme in melanin production. This helps to reduce the formation of excess pigment and can lead to a more even skin tone.
References
- Fitton, A., & Goa, K. L. (1991). Azelaic Acid. Drugs.
- Gollnick, H., & Schramm, M. (1998). Topical drug treatment in acne. Dermatology.
- Passeron, T., et al. (2019). Melasma treatment: A novel approach using a topical agent that contains an anti-estrogen and a low-dose retinoid. G Ital Dermatol Venereol.
- Wolf, J. E., Kerrouche, N., & Arsonnaud, S. (2006). Efficacy and safety of once-daily metronidazole 1% gel compared with twice-daily azelaic acid 15% gel in the treatment of rosacea. Cutis, 77(4 Suppl), 3-11.
- Hollinger, J. C., Angra, K., & Halder, R. M. (2018). Are natural ingredients effective in the management of hyperpigmentation? A systematic review. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology, 11(2), 28.
Alpha Arbutin
Alpha Arbutin is a derivative of hydroquinone and a biosynthetic active ingredient. Its primary action is inhibiting tyrosinase, a key enzyme involved in the synthesis of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Alpha Arbutin effectively reduces melanin production in the skin by inhibiting tyrosin activity. This gradually lightens hyperpigmented areas, such as age spots, melasma, and scars, resulting in a more even skin tone.
One of the significant advantages of Alpha Arbutin over other skin-lightening agents is its safety profile. Unlike hydroquinone, which has been associated with potential side effects and is restricted in many countries, Alpha Arbutin is considered safe and less irritating to the skin, even at higher concentrations. This makes it a suitable ingredient for all skin types, including sensitive skin.
In addition to its skin-lightening properties, Alpha Arbutin has also shown antioxidant effects, helping to protect the skin from oxidative stress caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
Physiological Effects
- Melanin Inhibition: Alpha Arbutin works by inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production in the skin. This action reduces the formation of melanin, leading to a lightening of skin pigmentation.
- Even Skin Tone: Regular use of alpha arbutin can lead to a more even skin tone overall, reducing the appearance of age spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Reduced Skin Discoloration: It effectively reduces the appearance of dark spots and areas of hyperpigmentation, such as those caused by acne, sun damage, or hormonal changes.
- Safer Alternative to Hydroquinone: While structurally similar to hydroquinone, alpha arbutin is a safer option with a lower risk of side effects.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Hyperpigmentation: Alpha arbutin treats melasma, sun spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne.
- Skin Brightening: Provide a more radiant and uniform skin tone.
- Anti-Aging: Reduce the appearance of age-related spots and uneven skin tone.
Bakuchiol
Bakuchiol's mechanism of action is similar to retinol's; it stimulates collagen production and accelerates cell turnover, improving skin texture and tone. It also helps reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation, making it an effective ingredient in anti-aging skincare products.
One of the key advantages of bakuchiol over traditional retinol is its gentleness on the skin. Retinol is known for potential side effects like dryness, redness, and irritation, particularly in sensitive skin or when used in high concentrations. Bakuchiol, however, is far less irritating. In addition to its anti-aging properties, bakuchiol exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, further contributing to its skin benefits. It helps protect the skin from oxidative stress and can soothe it, reducing redness and inflammation.
Bakuchiol's retinol-like effects and its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties make it an effective ingredient for various skin concerns, especially for those seeking natural alternatives in anti-aging and acne treatment.
Physiological Effects
- Retinol-like Function: Bakuchiol mimics the actions of retinol, stimulating collagen production. This helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improves skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Properties: It offers antioxidant benefits, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Bakuchiol has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help soothe the skin and reduce redness and irritation.
- Improved Skin Tone and Texture: Regular use of bakuchiol can improve skin tone and texture, making it smoother and more even.
- Acne Management: Bakuchiol's antibacterial properties and ability to regulate sebum production make it effective in managing acne.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Bakuchiol is popular in anti-aging skincare because it stimulates collagen production and reduces signs of aging.
- Sensitive Skin: As a gentler alternative to retinol, it is suitable for sensitive skin types that cannot tolerate traditional retinoids.
- Acne-Prone Skin: Its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties are beneficial in acne treatments.
- Hyperpigmentation: Bakuchiol can help treat hyperpigmentation, enhance skin radiance, and reduce dark spots.
References
- Chaudhuri, R. K., & Bojanowski, K. (2014). Bakuchiol: a retinol-like functional compound revealed by gene expression profiling and clinically proven to have anti-aging effects. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Dhaliwal, S., et al. (2019). Prospective, randomized, double-blind assessment of topical bakuchiol and retinol for facial photoageing. British Journal of Dermatology.
- Sivamani, R. K., et al. (2019). Clinical efficacy of a bakuchiol, niacinamide and zinc pyrithione formulation in facial sebum control and mild acne. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.









SIZE: 30 mL

Even Skin Tone

Anti-Aging

Brightening

Exfoliating

smooth skin
Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is highly acclaimed for its remarkable exfoliating and rejuvenating properties. Its small molecular size enables deep skin penetration, fostering efficient exfoliation at the cellular level.
Glycolic acid’s water solubility allows it to penetrate the upper layers of the skin easily. Its primary mechanism of action involves weakening the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their shedding, and revealing the newer, healthier skin beneath. This process of accelerated cell turnover is instrumental in addressing a range of skin concerns, from aging signs like fine lines and wrinkles to texture irregularities and hyperpigmentation.
Glycolic acid's efficacy extends beyond mere exfoliation. It's also recognized for stimulating collagen production, a crucial protein in maintaining skin's elasticity and firmness. This aspect contributes to its anti-aging benefits. Furthermore, its hydrating properties add to its appeal, as they help increase the skin's capacity to retain moisture, leading to a more supple and vibrant complexion.
Clinical studies have consistently supported glycolic acid's role in improving skin appearance. Research indicates significant improvements in skin texture and pigmentation and the visible reduction of wrinkles and fine lines with glycolic acid.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: Glycolic acid is a powerful exfoliant. It dissolves the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, facilitating their removal and revealing newer, healthier skin underneath.
- Increased Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for skin elasticity and firmness. This action helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Enhanced Skin Hydration: Glycolic acid improves the skin's ability to retain moisture, enhancing hydration and a more plump, vibrant skin appearance.
- Skin Brightening: Removing dead skin cells can brighten the complexion and reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Improved Skin Texture: Regular use of glycolic acid can lead to smoother, more even textured skin, making it beneficial for conditions like keratosis pilaris.
- Acne Treatment: Its exfoliating properties help in unclogging pores, thereby reducing the occurrence of acne breakouts.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Glycolic acid is widely used in anti-aging products to reduce signs of aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: It helps manage acne by exfoliating the skin and removing blockage from pores.
- Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats hyperpigmentation by accelerating the removal of hyperpigmented skin cells.
- Textural Irregularities: Glycolic acid can improve skin texture and is beneficial for treating keratosis pilaris and other conditions of rough skin.
- Sun-Damaged Skin: It helps rejuvenate sun-damaged skin by accelerating cell turnover and collagen synthesis.
References
- Bernstein, E. F. (2001). Glycolic acid treatment increases type I collagen mRNA and hyaluronic acid content of human skin. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Sharad, J. (2013). Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 35(3), 388-391.






SIZE: 50 mL

Antioxidant

anti-aging

DNA repair

sun protection

Moisturizing
Coenzyme Q10
CoQ10 is a potent ingredient that offers comprehensive skin health and appearance benefits. Its role in energy production and its antioxidant and anti-aging properties make it invaluable for photoprotection, anti-aging, and overall skin vitality. Its incorporation into DermExcel sunscreen represents a holistic approach to skin health, addressing protective and restorative needs.
Physiological Impact
- Skin Barrier Enhancement: CoQ10 contributes to the strength and health of the skin barrier, improving its ability to retain moisture and protect against external irritants and pollutants.
- Skin Repair and Regeneration: It supports the skin's natural ability to repair itself and regenerate, maintaining a healthy, youthful appearance. This is particularly beneficial in mature skin, where natural levels of CoQ10 may be depleted.
Pharmacological Advantages
- Anti-Aging Effects: CoQ10's antioxidant properties contribute to its anti-aging effects. By reducing oxidative stress, it helps to minimize the visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles and fine lines.
- Photoprotection: It enhances the skin's defense against photoaging caused by exposure to UV rays. CoQ10 helps to mitigate the degradation of collagen and elastin, proteins essential for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness.
Biochemical Benefits
- Cellular Energy Production: CoQ10 plays a crucial role in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, which is essential for the production of ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell. This function is vital for maintaining the health and vitality of skin cells.
- Antioxidant Properties: It acts as a lipophilic antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and preventing oxidative damage to cell membranes, proteins, and DNA. This is particularly important in the skin, which is frequently exposed to oxidative stress from environmental factors like UV radiation.
Vitamin E
The fat-soluble Vitamin E's benefits in maintaining skin health and appearance are well-acknowledged in both cosmetic and clinical dermatology. Comprising a group of eight compounds, including four tocopherols and four tocotrienols, Vitamin E is known for its role in protecting cell membranes from oxidative damage.
Vitamin E is celebrated in skincare for its ability to neutralize free radicals caused by environmental stressors such as UV radiation and pollution. These free radicals can lead to premature skin aging, making Vitamin E a valuable ingredient in anti-aging skincare products. Its antioxidant action helps to protect the skin from damage, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and improve skin texture and tone.
Additionally, Vitamin E is known for its moisturizing benefits. It helps to strengthen the skin barrier, reduce moisture loss, and keep the skin hydrated and supple. This makes it especially beneficial for dry and damaged skin.
Vitamin E also has anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial in soothing and calming irritated skin. This has implications for conditions such as dermatitis and acne, where inflammation plays a key role.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Protection: Vitamin E neutralizes harmful free radicals in the skin, preventing oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
- Moisturization: It has moisturizing properties, helping to improve skin hydration and alleviate dryness.
- Wound Healing: Vitamin E may assist in the skin's healing process, although its efficacy in wound healing is still a subject of research.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it can provide some degree of photoprotection by strengthening the skin's defense against UV-induced damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: It helps reduce skin inflammation and is beneficial in managing conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Its antioxidant properties make it useful in anti-aging skincare products to protect against free radical damage and improve skin appearance.
- Dry Skin Conditions: Vitamin E's moisturizing effects are beneficial in treating dry skin and improving overall skin texture.
- Inflammatory Skin Diseases: It can be helpful in soothing inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
- Sun Protection and Repair: Vitamin E is included in sunscreens and after-sun products for its ability to mitigate sun damage.
- Scar Treatment: Some studies suggest Vitamin E may help reduce the appearance of scars, although evidence is mixed.
References
- Thiele, J. J., Hsieh, S. N., & Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S. (1998). Vitamin E: Critical Review of Its Current Use in Cosmetic and Clinical Dermatology. Dermatologic Surgery, 24(7), 805–813.
- Ratz-Łyko, A., & Arct, J. (2016). Anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties of active skin care ingredients. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 9(9), 36–40.
- Keen, M. A., & Hassan, I. (2016). Vitamin E in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal.
- Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S., & Thiele, J. (2007). Vitamin E in human skin: Organ-specific physiology and considerations for its use in dermatology. Molecular Aspects of Medicine.
- Nachbar, F., & Korting, H. C. (1995). The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin. Journal of Molecular Medicine.
Broad Spectrum Filters
Tinosorb® M and Tinosorb® S represent sophisticated advancements in sun protection technology.
Tinosorb® M
- Biochemical Action: A unique UV filter due to its ability to function through absorption, reflection, and scattering of UV rays.
- Physiological Impact: The triple-action mechanism of Tinosorb® M offers comprehensive sun protection. By mitigating the penetration of both UVA and UVB rays, it significantly reduces the risk of DNA damage, photoaging, and carcinogenesis. Its ability to remain on the skin's surface reduces systemic exposure, making it a safer option with minimal potential for irritation or allergic reactions.
Tinosorb® S
- Biochemical Action: A broad-spectrum UV filter with a molecular structure that effectively absorbs both UVA and UVB rays. Additionally, it enhances the photostability of other UV filters, making the sunscreen formulation more effective over time.
- Physiological Impact: By providing extensive UVA and UVB protection, Tinosorb® S plays a crucial role in preventing short-term sun damage like sunburn and long-term risks such as skin aging and skin cancer. Its photostability ensures sustained protection during sun exposure, and its compatibility with other UV filters means it can be used to formulate sunscreens that are both effective and suitable for sensitive skin.
Sunscreen
Using sunscreen is a fundamental aspect of skin care and preventive dermatology. It's essential for reducing the risk of skin cancers and photoaging and maintaining overall skin health in the face of constant exposure to UV radiation.
Sunscreen is a vital skincare product designed to protect the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Two primary types of UV radiation affect the skin: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and are primarily responsible for aging and long-term skin damage, whereas UVB rays cause sunburn and play a key role in developing skin cancer.
Sunscreen products work by either absorbing, reflecting, or scattering sunlight. They contain chemical compounds that absorb UV radiation and convert it into a small amount of heat or physical compounds (like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) that act as a physical barrier, reflecting UV light away from the skin.
The effectiveness of sunscreen is measured by its Sun Protection Factor (SPF). SPF indicates how well the sunscreen protects against UVB rays. For example, an SPF of 30 means it would take 30 times longer for your skin to burn than without sunscreen. However, it's important to note that no sunscreen can block 100% UV rays.
Regular use of sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 can reduce the risk of skin cancer, prevent sunburn, and slow down the skin's aging process.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Prevention of Sunburn: Sunscreen protects the skin from UVB rays, which cause sunburn. This reduces the immediate risk of skin damage and discomfort.
- Skin Cancer Prevention: Regular use of sunscreen significantly lowers the risk of developing various types of skin cancer, especially melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma.
- Prevention of Photoaging: Sunscreen also shields the skin from UVA rays, which penetrate deeper into the skin and are primarily responsible for photoaging, including wrinkles, leathery skin, and sunspots.
- Protection Against Photosensitivity: Sunscreen helps prevent flare-ups triggered by sun exposure for individuals with photosensitive skin conditions like lupus or rosacea.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: It aids in preventing and managing hyperpigmentation and melasma, conditions exacerbated by sun exposure.
- General Skin Health: Sunscreen helps maintain overall skin health and integrity by protecting the skin from UV damage.
References
- Burnett, M. E., & Wang, S. Q. (2011). Current sunscreen controversies: a critical review. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine.
- Green, A. C., et al. (2011). Reduced melanoma after regular sunscreen use: randomized trial follow-up. Journal of Clinical Oncology.
- Hughes, M. C. B., et al. (2013). Sunscreen and Prevention of Skin Aging: A Randomized Trial. Annals of Internal Medicine.